Materials processing by laser ablation and surface modification enables the flexible fabrication of micro- and nano-structures for challenging applications in a row of contemporary technology areas. Innovative beam delivery concepts allow sub-µm precision, if laser wavelength and pulse duration are suitably selected. The fabrication of structural details of the order of 50 nm are possible.
In this field, ultrashort laser pulses are gaining a rapidly increasing importance for a range of emerging applications. Although compact, industrial-scale short pulse laser systems are commercially available, for a sustainable growth of this technology field it is essential to further develop various short pulse-based techniques. This is one of the main objectives of our department. A special emphasis is put on the generation of energetic ultrashort pulses, particularly in the ultraviolet spectral range, and the fabrication of periodic nanostructures on technical surfaces.
Our activities include the study of dynamics of laser ablation of solid surfaces by ultrashort UV pulses, the direct writing of complex holographic security features and the surface functionalization of technologically important materials. Further research is focused on the nano-patterning of metal surfaces, thin metallic films, and transparent materials. Laser induced structure formation on the nanometer scale as well as the fabrication and characterization of metal and semiconductor nanoparticle films are also investigated.
Ultrashort pulses
Ultrashort pulse lasers offer the unique capability of extreme concentration of energy in time and space. Such sources allow the generation of very high intensities while delivering only moderate energies in a well-controlled manner. Therefore the ultrashort-pulse laser technology holds great potential for applications in a row of contemporary technology branches. Related objectives of our department are the generation of energetic ultrashort pulses, particularly in the ultraviolet spectral range.
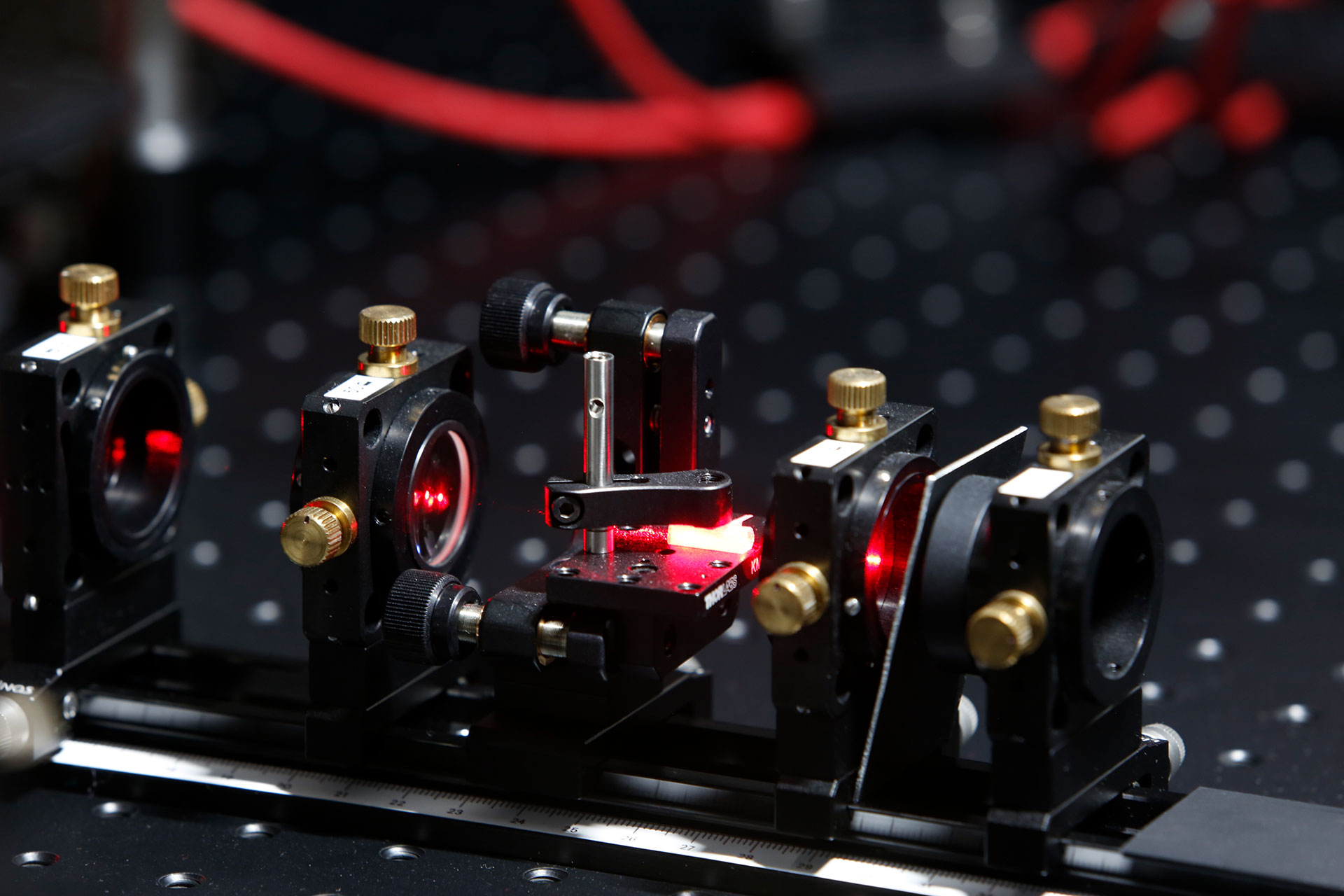
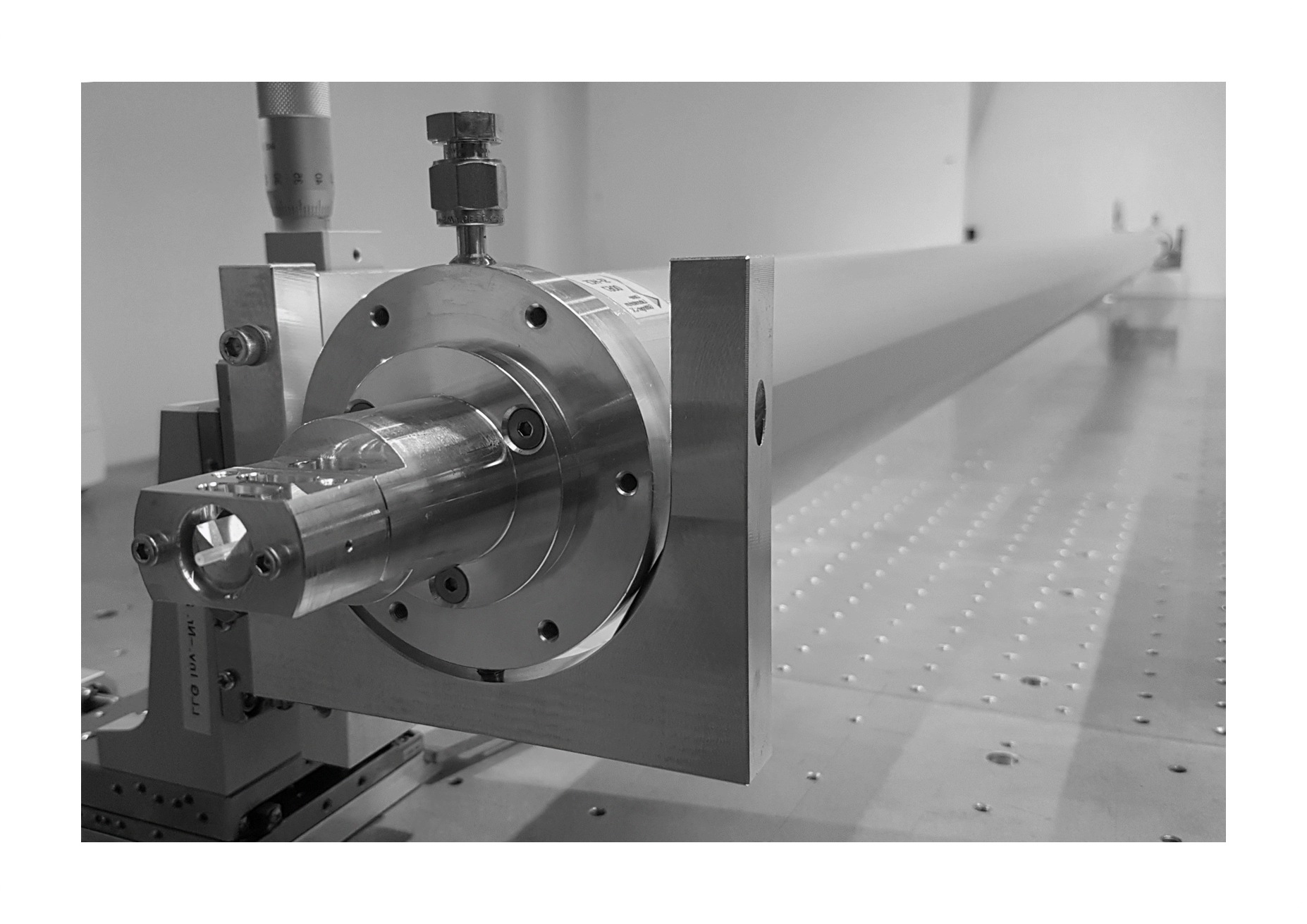
Stretched flexible hollow fiber
In our institute, the fundamentals of a new type of hollow fiber device for the compression of ultra-short pulses were laid more than ten years ago, and the technology has been continuously developed since then. The technique is based on stretching of flexible hollow fibers, thus achieving unsurpassed straightness even for long lengths, which is essential for a large number of core parameters (power, transmission and compression factor). Several record results have been achieved with this novel fiber device in recent years.
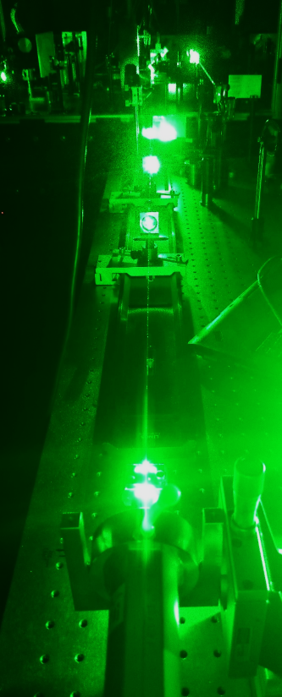
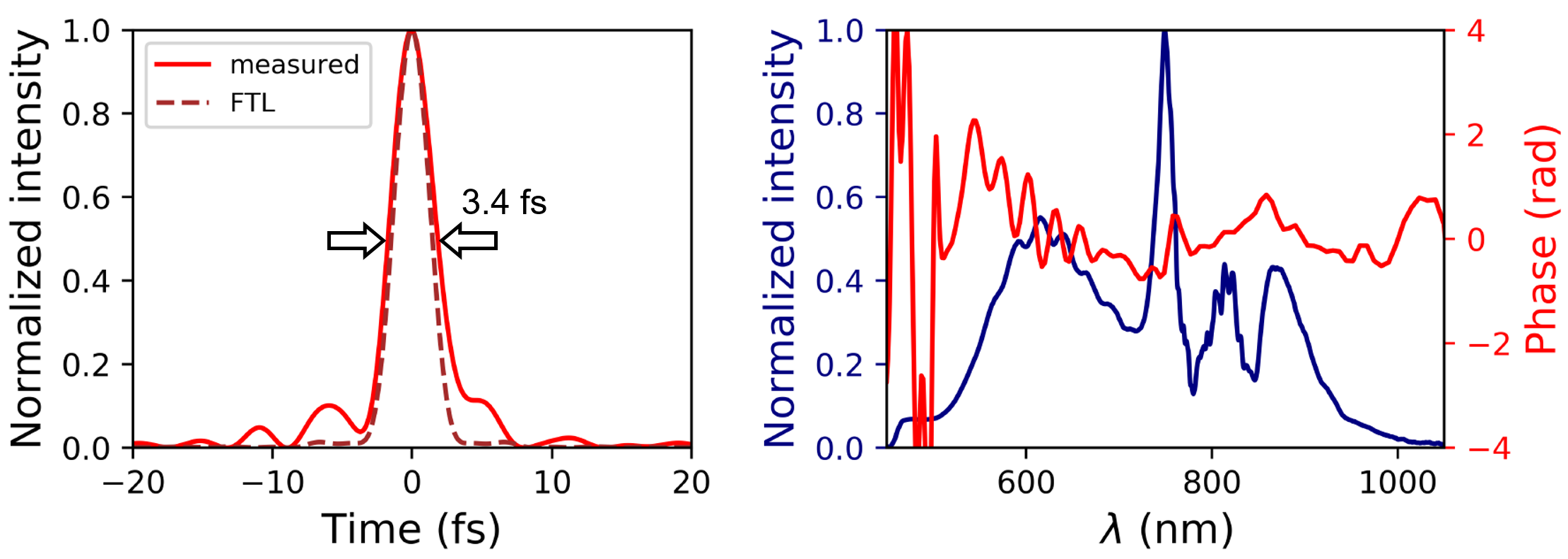
In collaboration with researchers from the Laboratoire d’Optique Appliquée (LOA), CNRS, Ecole Polytechnique, ENSTA Paris and the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy, we have successfully applied the technology for the compression of pulses to reach extremely high peak intensities. The laser system operated at the LOA in Paris, in which our hollow fiber is integrated, delivers pulses with a peak power of up to 1 TW, a pulse duration of 3.4 fs and excellent beam quality. This laser system is currently the only one in the world that is able to generate CEP-stable sub-4-fs pulses with TW peak power at kHz repetition rate. Thus, this laser source is suitable for the investigation of relativistic light-matter interaction effects on the sub-cycle time scale.
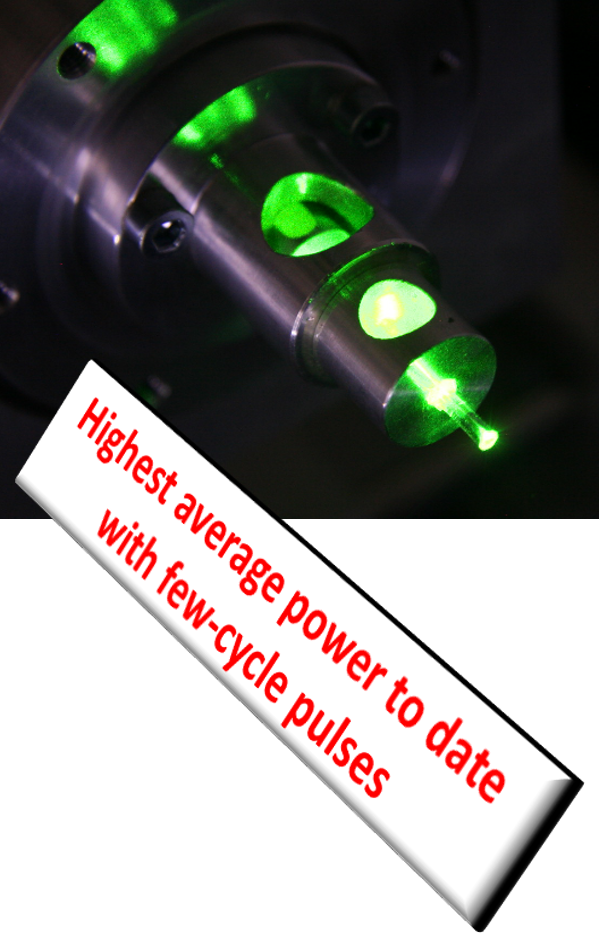
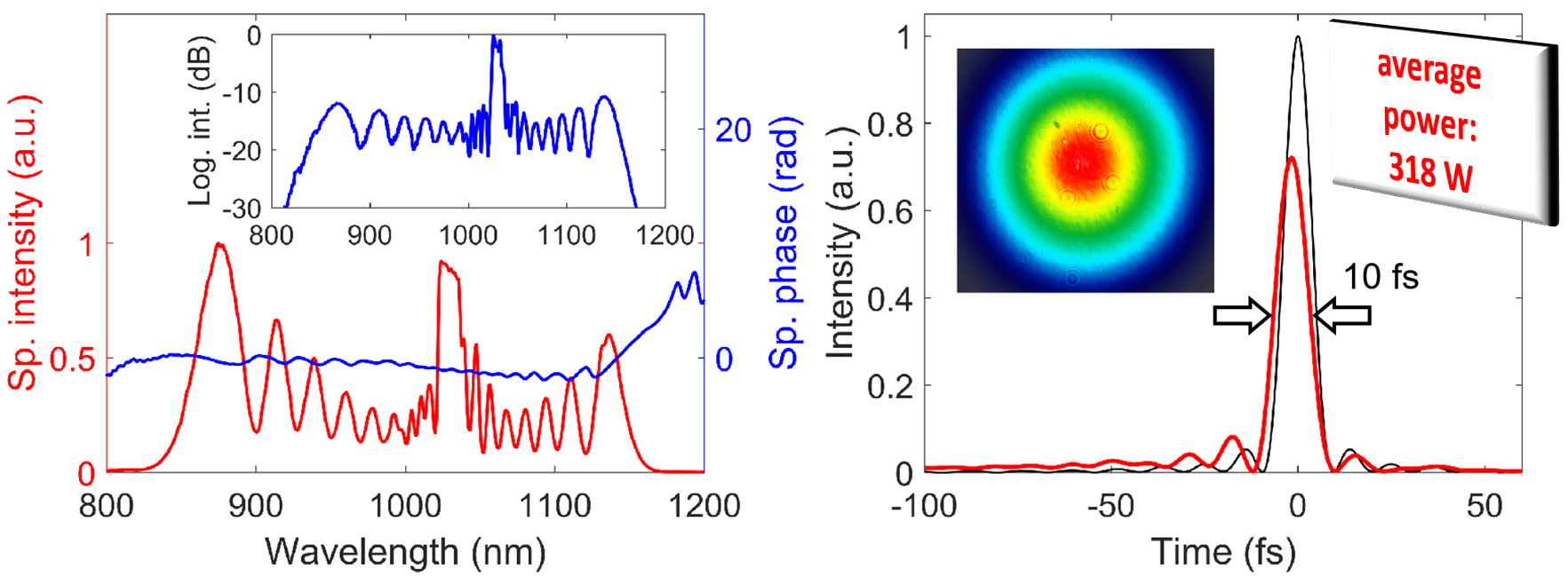
In a further collaboration with the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI, Berlin) and the Active Fiber Systems GmbH (AFS GmbH, Jena), generation of a train of 10 fs pulses, carrying 3.2 mJ at a repetition rate of 100 kHz, delivering an average power of over 300 W was achieved. This groundbreaking result was made possible by combining two leading technologies. A laser system, currently under development at AFS GmbH for the major European laser facility ELI ALPS in Szeged, Hungary, uses the coherently combined multi-channel fiber amplifier technology to generate high power pulses. This system was then complemented by the stretched flexible hollow fiber compression technology, developed by IFNANO and MBI, to obtain record-breaking compression and control of high power pulses.
The achieved world record values constitute a major breakthrough of the hollow fiber compression scheme, indicating that industry-grade high power laser radiation can reach the few-cycle regime.
Further information:
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
“Generation of 200-µJ, sub-25-fs deep-UV pulses using a noble-gas-filled hollow fiber”, Opt. Lett. 34, 2300 (2009) - T. Nagy, V. Pervak, P. Simon:
Optimal pulse compression in long hollow fibers, Opt. Lett. 36 (2011), 4422 - F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo, U. Morgner, P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
“Compression of CEP-stable multi-mJ laser pulses down to 4 fs in long hollow fibers”, Laser Phys. Lett. 11 095401 (2014) - B.-H. Chen, M. Kretschmar, D. Ehberger, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, P. Baum, T. Nagy:
Compression of picosecond pulses from a thin-disk laser to 30fs at 4W average power, Optics Express 26, 3861 (2018) - T. Nagy, P. Simon:
„Generation of 200-µJ, sub-25-fs deep-UV pulses using a noble-gas-filled hollow fiber“, Opt. Lett. 34, 2300 (2009) - T. Nagy, V. Pervak, P. Simon:
Optimal pulse compression in long hollow fibers, Opt. Lett. 36 (2011), 4422 - F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo, U. Morgner, P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
„Compression of CEP-stable multi-mJ laser pulses down to 4 fs in long hollow fibers“, Laser Phys. Lett. 11 095401 (2014) - B.-H. Chen, M. Kretschmar, D. Ehberger, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, P. Baum, T. Nagy:
Compression of picosecond pulses from a thin-disk laser to 30fs at 4W average power, Optics Express 26, 3861 (2018) - N. G. Khodakovskiy, M. P. Kalashnikov, V. Pajer, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, M. M. Toktamis, M. Lozano, B. Mercier, Z. Cheng, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens: “Generation of few-cycle laser pulses with high temporal contrast via nonlinear
- T. Nagy, S. Hädrich, P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, N. Walther, R. Klas, J. Buldt, H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, I. Seres, Z. Várallyay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
“Generation of three-cycle multi-millijoule laser pulses at 318 W average power”, Optica 6, 1423 (2019) - M. Ouillé, A. Vernier, F. Böhle, M. Bocoum, A. Jullien, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, Z. Cheng, D. Gustas, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, S. Haessler, J. Faure, T. Nagy R. Lopez-Martens:
“Relativistic-intensity near-single-cycle light waveforms at kHz repetition rate”, Light Sci Appl 9, 47 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0280-5 - T. Nagy, P. Simon, L. Veisz:
High-energy few-cycle pulses: post-compression techniques, Advances in Physics: X, 6:1, 1845795, DOI: 10.1080/23746149.2020.1845795 - 46149.2020.1845795
Short pulse laser development
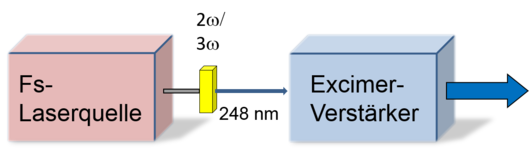
The system architecture for the generation of energetic femtosecond pulses in the UV is displayed below. Pulses out of a commercially available short pulse laser source (e.g. a Ti:sapphire oscillator/amplifier arrangement) are frequency tripled to 248.5 nm and then amplified in a special excimer amplifier module. Depending on custom requirements such a module can be optimized for different performance characteristics.
High intensities
The generation of high intensities requires high pulse energies, a short pulse duration and excellent beam focusability. In this respect, a fundamental advantage of UV laser sources is their capability to focus the radiation much tighter than IR devices can do (focal area ~ λ2). UV high brightness laser systems apply excimer modules to amplify the frequency converted radiation of conventional short pulse lasers. A specific advantage of excimer amplifiers is offered by their low density amplifying medium, insuring negligible phase front distortions during amplification, thus resulting in excellent output beam quality.
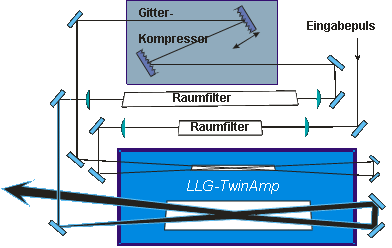
In order to meet the high demands of reaching highest intensities in the UV, a special twin-tube amplifier device was designed with two discharge channels. A spatial filter implemented between the discharge tubes provides very efficient ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) suppression. Furthermore, a grating pulse compressor applied to the pulses in front of the second discharge tube allows control of the temporal pulse profile at relatively modest energy levels. This system architecture results in output pulse energies of up to 50 mJ with a typical pulse duration of 250 fs with excellent beam quality, thus enabling to reach focused intensities of ~ 1019 W/cm2.
High pulse energies
High pulse energies If a specific application requires the highest possible pulse energy out of a UV femtosecond laser, the main emphasis should be placed on the optimization of the energy extraction efficiency in the excimer power amplifier module. This can be accomplished by applying the so called interferometric multiplexing scheme.
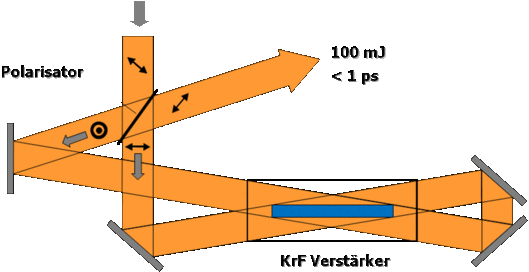
The energy storage time of a KrF amplifier is typically 2-3 ns. Consequently, subsequent replenishment of the gain in every 3 ns within the entire gain lifetime (app. 15 ns) of the amplifier is possible. This means, that a train of 2 or 4 femtosecond pulses can be propagated through the amplifier, and all of the pulses will extract the same amount of energy from the amplifier. After passage through the gain module, the pulses are then recombined at the output. This should be done with interferometric precision in order to maintain the femtosecond pulse duration and the diffraction limited beam quality. Standard multiplexing schemes do not offer the required precision; therefore we introduced a new scheme which ensures phase locked superposition of the pulses upon demultiplexing.
A polarizer subdivides the input pulse into orthogonally polarized components, which propagate through the amplifier along the same optical path in reversed directions. Recombination of the pulses occurs at the same polarizer which is used for beam splitting. Applying the multiplexing scheme to an amplifier module of the type „LLG50“, the available output energy reaches 100 mJ with a subpicosecond pulse duration.
Further information:
S. Szatmári, P. Simon: Interferometric multiplexing scheme for excimer amplifiers, Optics Commun. 98, 181 (1993).
J. Békési, G. Marowsky, S. Szatmári and P. Simon: A 100 mJ table-top short pulse amplifier for 248 nm using interferometric multiplexing, Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 215, 12, 1543 (2001)
High average power
Many applications (like industrial scale material processing) require a high average power of the applied laser pulses. This can only be realized using high repetition rate systems. To this aim we converted an industrial excimer laser („NovaLine 100“ of Coherent Lambda Physik) into a short pulse amplifier. This model has a sufficiently large discharge volume and delivers an average power of 100 W at a rep rate of 250 Hz in the standard nanosecond mode. With appropriate modifications of the discharge chamber and the high voltage charging circuit, amplification of seed pulses of a frequency converted Ti:sapphire laser beam up to 30 mJ/pulse at repetition rates in excess of 300 Hz has been demonstrated. The resulting average power of ~10 W is the highest value to date achieved by a table-top deep UV femtosecond laser system.
Further information:
J. Békési, S. Szatmári, P. Simon, G. Marowsky:
Table-Top KrF Amplifier Delivering 270 fs Output Pulses with over 9 W Average Power at 300 Hz, Appl. Phys. B. 75, 521-524 (2002)
Laser induced nanostructure formation
The removal of material by intense, pulsed laser irradiation is termed laser ablation or photoablation. Understanding the complex phenomena of this process, it can be utilized for the controlled micro- and nanopatterning of material surfaces. The ablation dynamics of metals, semiconductors, and dielectrica and the corresponding structure formation on the nanometer-scale are investigated. In addition to laser ablation, various processes of laser induced material modification are possible. Examples are chemical modification, laser induced material transfer or implantation. The laser induced formation of plasmonic nanoparticles and light-emitting nanocrystals are treated as well.
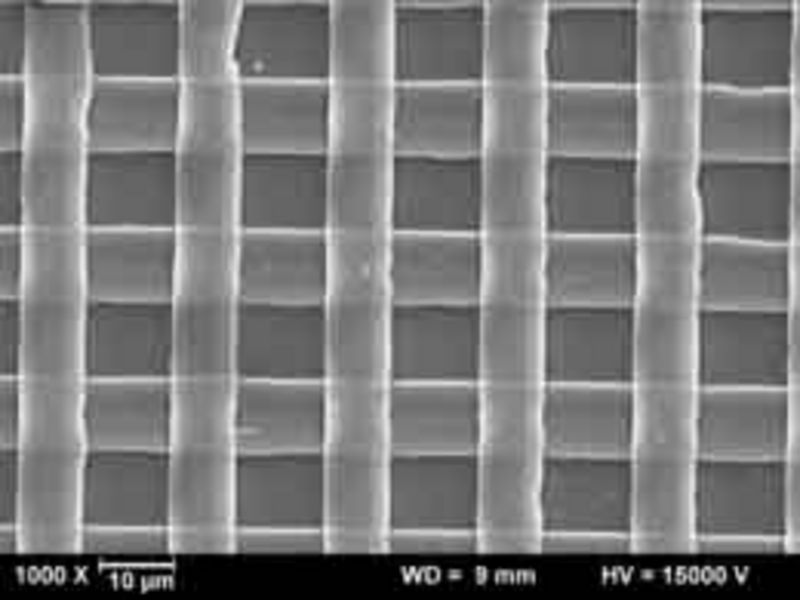
Silica nano grid
Transparent Materials
Precise, high-resolution laser patterning of glass materials is still a challenging task. As glass is transparent in the visible and the near UV spectral range, for the ablative structuring of glass IR or deep-UV lasers are applied. As the achievable resolution scales with the wavelength, IR light does not provide the spatial resolution required for µm- and sub-µm-patterning. Hence, lasers emitting in the deep-UV are preferentially used for fast and high-resolution patterning of glass. While some lead-containing glasses exhibit sufficient absorption at 248 nm, most standard silicate glasses require a laser wavelength below 200 nm for efficient absorption. The ArF-excimer laser emitting at 193 nm is optimally suited to obtain controlled, crack free patterns with high resolution. At this wavelength, surface relief gratings in doped and pure glass have already been successfully fabricated. Such periodic patterns have a number of applications, e.g. for surface functionalization or diffractive marking.
Further information:
M. Wiesner, J. Ihlemann:
High resolution patterning of sapphire by F2-laser ablation Applied Physics A 103, 51 (2011)
R. Karstens, A. Gödecke, A. Prießner, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of 250-nm-hole arrays in glass and fused silica by UV laser ablation Optics and Laser Technology 83, 16 (2016)
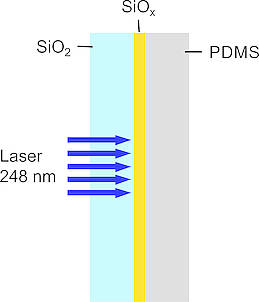
Dielectric layers
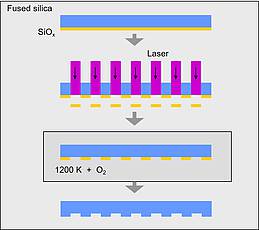
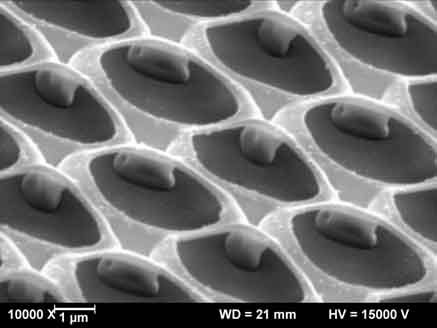
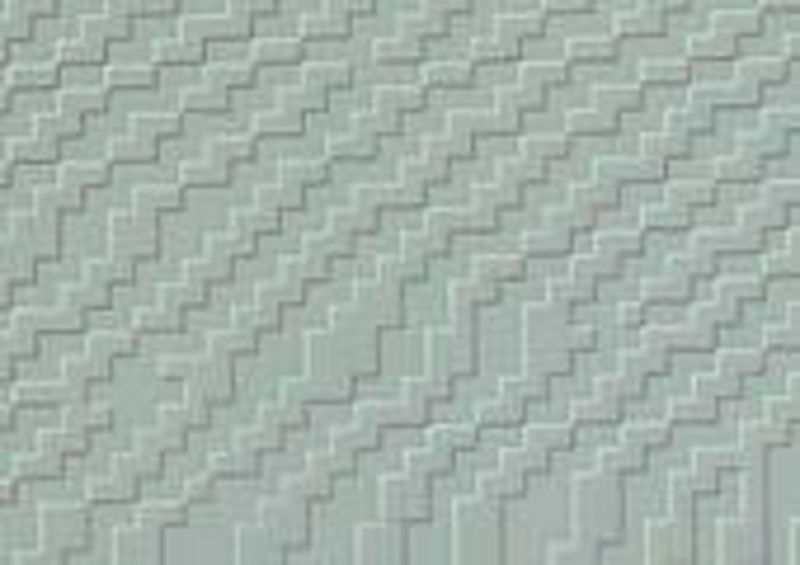
Silicon suboxide films (SiOx) can be structured by laser irradiation in manifold ways. Besides film ablation and film transfer, a laser induced transformation process resulting in a complex geometry is possible. A controlled, reproducible forming will be accomplished, if on top of the SiOx-film (coated on a transparent fused silica substrate) a polymeric superstrate (confinement layer) is deposited. Thus, rear side irradiation of the film through the substrate leads to partial melting of the SiOx-film and subsequent resolidification in a well-defined shape. An unrestricted melt movement leading to irregular patterns is prevented by this confinement. Precondition for a complete forming of the film is a combination of absorption coefficient and thickness of the SiOx-film resulting in “melting”, i.e. a sufficient reduction of the viscosity across the whole film thickness. According to film- and irradiation parameters, a variety of shapes can be obtained like humps, blisters, cups, or grids of SiOx-material. A special feature of these grids is the undiminished adhesion of the film in the non-irradiated areas and the undercut straps in between, which cannot be produced by conventional laser or etch processes. Pure quartz grids are obtained by subsequent high temperature annealing (oxidation of SiOx to SiO2). Various applications in the fields of optics, micro and nano fluidics, or life science are imaginable.
Further information:
J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
Pulsed laser-induced formation of silica nanogrids Nanoscale Research Letters 9, 102 (2014)
T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Silicon suboxide (SiOx): laser processing and applications Appl. Phys. A 117, 13 (2014)
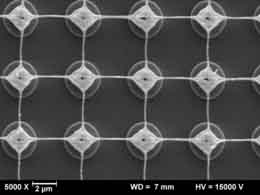
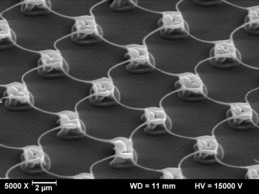
SiO2 nano grid
Si-Nanocristalle
Silicon nanocrystals (Si-NC) are of interest as integrated light emitters in silicon based photonics. They are mainly fabricated by high temperature annealing of substoichiometric SiOx, also known as silicon-rich silicon oxide, leading to a phase separation into Si and SiO2. Strong visible to infrared photoluminescence of clusters and nanocrystals is attributed to quantum confinement and defect states at the boundary between nanocrystal and surrounding matrix. Compared to conventional furnace annealing, laser annealing offers the possibility to generate nanocrystals locally controlled. Furthermore, the thermal load of the substrate can be reduced, thereby allowing materials and components that do not permit high temperatures. The main problem of the laser annealing process is the collateral damage of the film structure, ruling out this process for device fabrication up to now. Applying a continuous wave laser emitting at 405 nm for laser induced phase separation in SiOx films, the formation of Si-nanocrystals in substrate bound films without degrading the optically smooth surface has been accomplished. Such conditions are necessary for fabricating devices like waveguides for photonic applications.
Futher Information:
T. Fricke-Begemann, N. Wang, P. Peretzki, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Generation of silicon nanocrystals by damage free continuous wave laser annealing of substrate-bound SiOx films
Journal of Applied Physics 118, 124308 (2015)
N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
Formation of porous silicon oxide from substrate-bound silicon rich silicon oxide layers by continuous-wave laser irradiation,
Journal of Applied Physics 123, 093104 (2018)
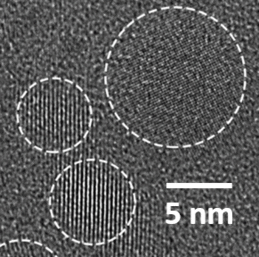
Laser generated Si nanocrystals
Plasmonic particles
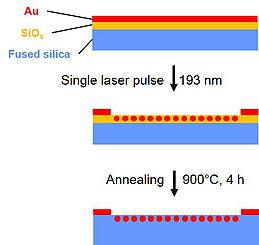
The generation and controlled arrangement of metallic nanoparticles is very important for the fabrication of plasmonic components. Arrays of gold or silver nanoparticles are used for instance as substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The plasmonic resonance of these noble metal particles enables high sensitivity for excitation in the visible spectral range. However, due to their little adhesion to glass, for many applications nanostructured gold or silver films on top of the substrate do not exhibit sufficient stability. Therefore, concepts for embedding particles partially or completely in the near-surface glass material are desired. Performing pulsed UV-laser irradiation of thin noble metal films deposited on glass substrates at sufficiently high fluence, the incorporation of metal particles in the glass is observed. This process is called laser implantation.
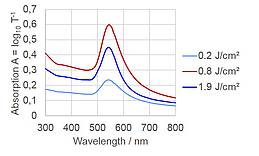
For the implantation of gold into pure fused silica, fluences of about 1 J/cm² at 193 nm laser wavelength are required. Using a SiOx (x ≈ 1) coated SiO2-substrate, the implantation of gold into this coating can be accomplished at significantly lower fluences starting from 0.2 J/cm². Particles with diameters in the range of 10 to 60 nm are implanted to a depth of about 40 nm as identified by transmission electron microscopy. An additional high temperature annealing step in air leads to the oxidation of SiOx to SiO2, without influencing the depth distribution of the particles significantly. Absorption spectra show a characteristic plasmon resonance peak at 540 nm. Thus, pure silica glass (SiO2) with near surface incorporated plasmonic particles can be fabricated with this method. Such material systems may be useful for example as robust substrates for plasmonic applications.
Further information:
H. Stolzenburg, P. Peretzki, N. Wang, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Implantation of plasmonic nanoparticles in SiO2 by pulsed laser irradiation of gold films on SiOx-coated fused silica and subsequent thermal annealing Applied Surface Science 374, 138 (2016)
M. Heinz, V.V. Srabionyan, L.A. Avakyan, A.L. Bugaev, A.V. Skidanenko, V.V. Pryadchenko,
J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, C. Patzig, M. Dubiel, L.A. Bugaev:
Formation and implantation of gold nanoparticles by ArF-excimer laser irradiation of gold-coated float glass, Journal of Alloys and Compounds 736, 152 (2018)
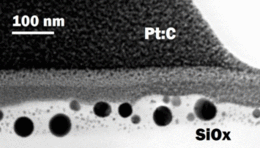
Gold nanoparticles implanted in quartz glass
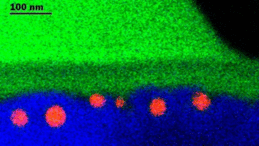
Rot: Gold, Blau: Glas, Grün: Umgebung
Study of the dynamics of UV femtosecond laser ablation
It is well known that material processing with ultrashort laser pulses provides a significantly increased precision compared to that achieved by standard technologies. The reason for this improvement is the onset of rapid structural changes of the irradiated material preceding its ablative removal. As a result, the material surrounding the irradiated region will be negligibly affected by heat diffusion, thus facilitating the creation of high resolution patterns. A full understanding of the fundamental microscopic mechanisms underlying the generation of nanostructures on surfaces is however still missing. On the other hand, this knowledge should help us to fabricate tailored surface structures with sub-100 nm resolution. This capability would open up new possibilities for the creation of particular functionalities. Firstly, our objective is to study the dynamics of the formation of periodic nano-structures. For their creation ultrashort UV pulses are used to insure the highest possible spatial resolution. An appropriate choice of the irradiated volume allows considering a limited number of atoms, thus making it feasible to describe the whole process by molecular dynamic simulation (in collaboration with the University Kassel and the TU Kaiserslautern). This strategy makes it possible for the first time to compare theory and experiment on the same temporal and spatial scale.
In the experiments, the structures with periods in the range of 270-500 nm are produced by a mask projection setup. By selecting only the ± 1st diffraction orders in the Fourier plane, we can ensure that a sinusoidal intensity distribution will be created on the sample surface. The laser pulses are delivered by a frequency tripled Ti:Sa system seeding a KrF excimer amplifier running at a wavelength of 248 nm with a pulse length of 1.6 ps.
The results show a good agreement between the simulated cross section of the irradiated area and the experimentally measured topology of the structured sample, with void formation below the surface and an uplift of material in the area above.
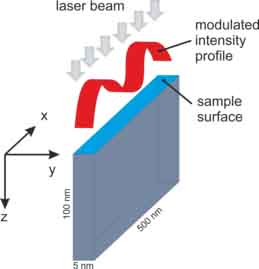
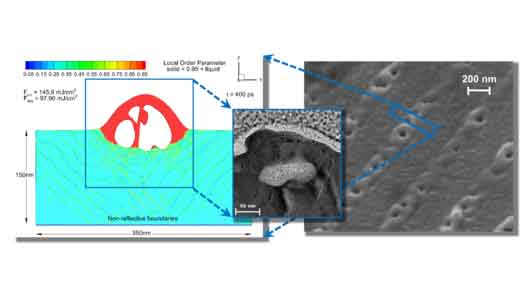
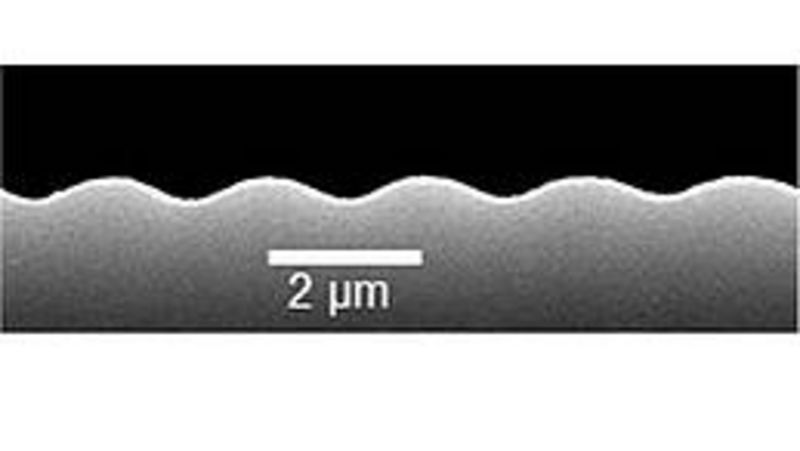
Novel geometry for the study of the ablation dynamics
Structured gold sample irradiated by a sinusoidal fluence distribution of ~ 145 mJ/cm² in average. Simulated cross section of the irradiated sample after 400 ps (left), transmission electron microscope recording of cross section (middle) and scanning electron microscope recording of the sample surface 45° tilted (right)
Glass and optics
The advancing miniaturization and the integration of diverse techniques and functionalities play an important role for the development of novel technologies and products. The fabrication of micro optical components and their integration into micro systems can often be accomplished by direct laser processing. The machining of glass materials usually requires wavelengths in the deep UV range (193 nm or 157 nm).
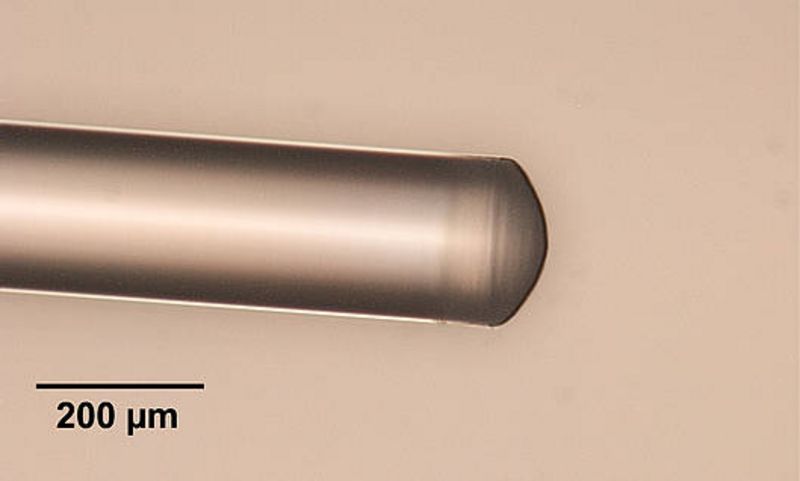
Quartz fiber lens
Micro lenses
Laser ablation enables the manufacturing of refractive or diffractive lenses of glass or plastics. In contrast to many other production technologies, the fabrication is possible even under complex geometrical constraints. For instance, micro lenses can be made directly on the tip of an optical fiber.
An important component in micro-optical modules are Fresnel lenses. Due to their flat design, they allow a low construction height in the range of a few micrometers and easy integration with planar surfaces for high integration density. An application example is the provision of optical interconnects for data communication systems. To enable fast data transfer, the electrical signals are converted by optoelectronic transceiver modules into optical signals and then fed into optical waveguides. For the efficient coupling between light sources, waveguides and detectors, micro lenses are required. The lenses need to be integrated into the electro-optical circuit boards or in so-called glass interposers.
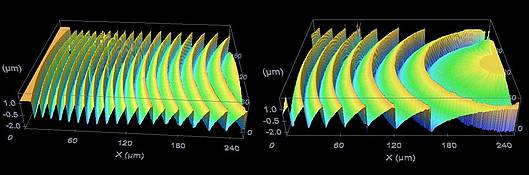
Height profile of a Fresnel lens
Further Information:
L. Brusberg, M. Neitz, H. Schröder, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Fresnel micro lens array in borosilicate glass by F2 laser ablation for glass interposer application,
Proc. SPIE 8951, 89510H (2014)
T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann
Hybrid micro-optical elements by laser-based fabrication of Fresnel lenses on the end face of gradient index lenses,
Optics Express 26, 23751 (2018)
Phase masks
Phase masks or phase plates from fused silica are used in various applications in the field of optics and photonics, e.g., in the form of diffractive masks for laser micro processing or for structured illumination or the generation of specific focus geometries in high-resolution microscopy. As fused silica cannot be patterned with sufficient precision by direct laser machining, a patented process using a precursor layer of silicon suboxide (SiOx) on a quartz glass substrate is applied. The thickness of the SiOxlayer has to match the required phase delay. To obtain the desired phase profile the UV absorbing layer is structured by spatially resolved laser ablation and converted into UV transparent SiO2 in a subsequent annealing process.In this way, a highly transparent and highly resistant mask made of pure quartz material is obtained. Precise process control based on optically measured layer parameters allows a precise adjustment of the phase delay with diffraction efficiencies close to the theoretical maximum.
Further information:
J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
Laser Based Rapid Fabrication of SiO2-phase Masks for Efficient UV-laser Micromachining,
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 4, 100 (2009)
J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, G. Danev:
Excimer laser ablation of thick SiOx-films: etch rate measurements and simulation of the ablation threshold,
Applied Physics Letters 101, 091901 (2012)
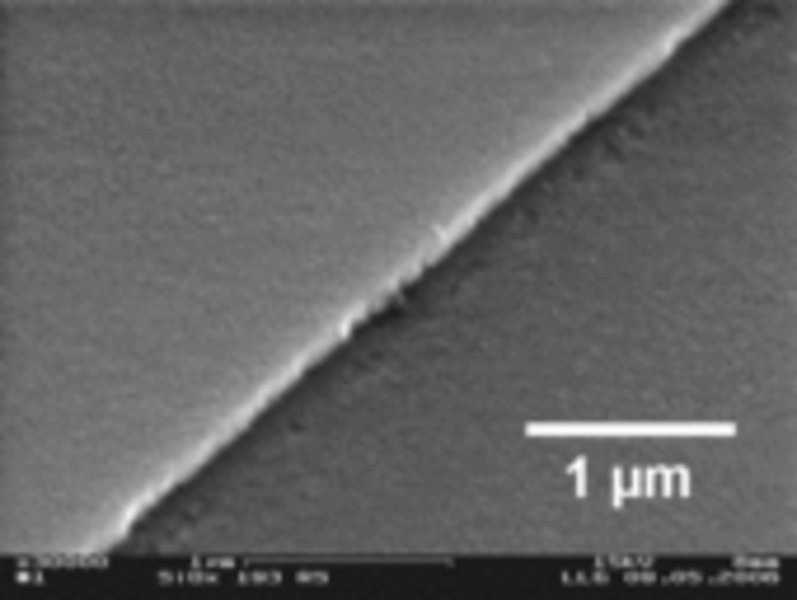
Ablation edge
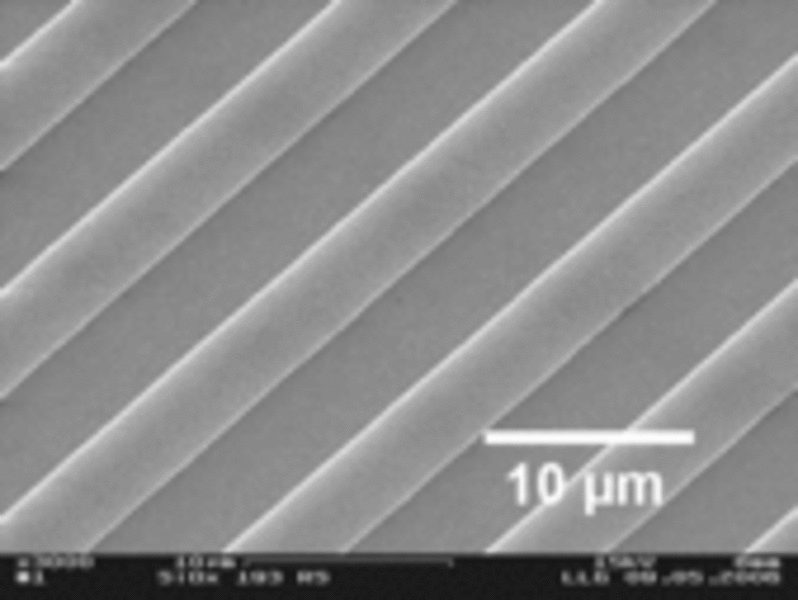
Laser ablation of SiOx-films

Two level phase element in fused silica
Additive manufacturing
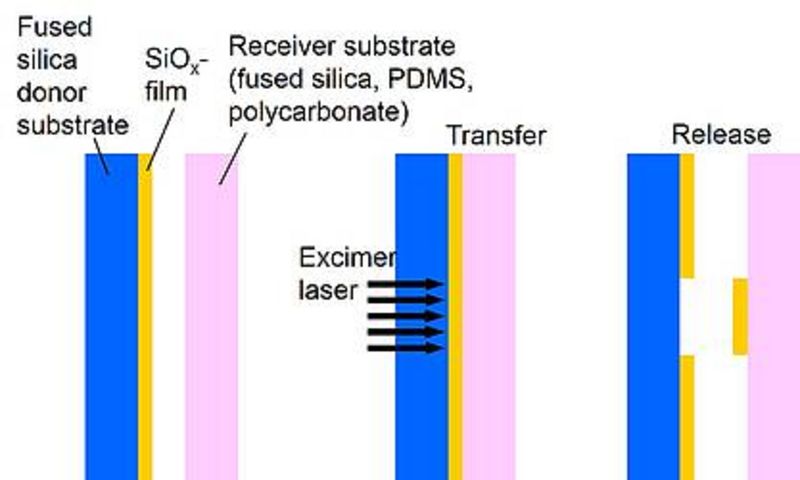
Well defined segments of silicon suboxide thin films deposited on fused silica substrates by vacuum evaporation are relocated to a receiver substrate by pulsed laser induced forward transfer. The receiver substrate (fused silica, silicone, or polycarbonate) is pressed against the SiOx-coated donor substrate, and the SiOx-film is irradiated through this transparent donor substrate with a single ArF or KrF excimer laser pulse. The shape of the transferred segments is defined by a projection mask. Films with a minimum thickness of 200 nm can be transferred this way. The process is a congruent transfer, i.e. the shape of the deposited film pad corresponds exactly to the ablated film segment defined by the mask. By repeated laser exposure after lateral displacement of the donor substrate (and appropriate rotation of the receiver substrate), stacking of film strips becomes possible, e.g. in form of a woodpile. A subsequent annealing step leads to oxidation to SiO2.
Furthermore, the arrangement of complex transparent structures can be accomplished by deposition, patterning and modification of silicone material.
Further Information:
J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
Patterned deposition of thin SiOx-films by laser induced forward transfer Thin Solid Films 550, 521 (2014)
A. Syring, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
F2-laser modification and patterning of silicone films Applied Surface Science 261, 68 (2012)
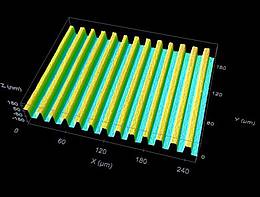
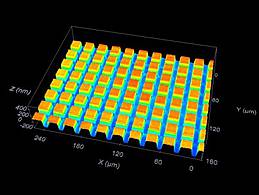
Periodic nanostructures
The study of periodic nanostructures is one of the leading topics of today’s photonics research. Such structures on the surface of metals, semiconductors, dielectrics or polymers can generate new material properties with very special electrical or mechanical characteristics. Depending on the specific material parameters and the morphology of the structures, new devices like micro-lasers, optical nano-switches, optical storage devices, bio-sensors or anti-fraud features can be realized. Furthermore, surface textures can be used to improve the tribological properties of special tools, for the reduction of reflection losses, to modify the wettability or the cell growth properties or as decoration elements for the refinement of precious goods.
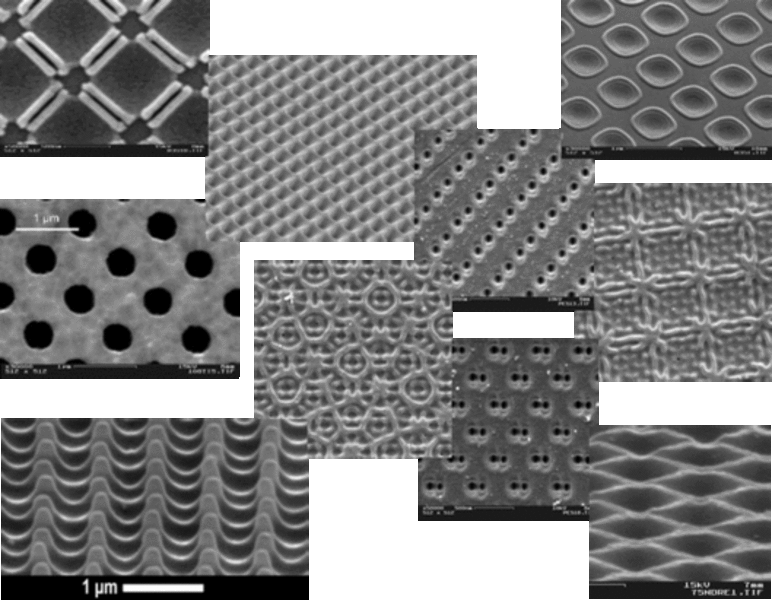
Diffractive marking (metals)
Diffractive laser direct patterning for direct writing of complex holographic security features on hardened steel and hard coatings
Diffractive Images and holographic security features are well suited for individual fraud resistant labeling of genuine parts. Due to their optically striking and high value appeal they can additionally be used as interesting design elements for an up-graded look of certain products. In most cases a direct integration of these structures into the surface of the part is of paramount importance. The application of holographic stickers in form of metalized polymer foils does not guarantee a secure permanent labelling and is not allowable for a variety of high-quality, massive metallic parts found e.g. in the automotive, aerospace or medical industry. Due to the high price for each sticker and the rather poor bonding with the plastic surface, the use of holographic stickers for security labelling of plastic parts is even more problematic. Instead, diffractive design elements or security labels must directly be integrated into the surface of the injection molding tool. Nowadays this can only be done via complex and expensive lithographic techniques (e. g. dry etching).
Therefore a new short pulse laser based direct patterning technology is currently developed within the framework of a joint research project funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research Economics and Technology. The novel technique enables diffractive laser writing of individual, complex, holographic security labels on metals and hard coatings with very high velocities. The technology is particularly suitable for the direct writing of holographic freatures into the surface of injection molding tools enabling the efficient and durable holographic marking of plastic parts.

Diffractive marking (glass)
Excimer lasers offer unique advantages for the processing of glass. Their short wavelengths in the ultraviolet spectral region are strongly absorbed by most glasses and offer an even higher spatial resolution than visible wavelengths. For most glass types, the use of the ArF excimer laser (wavelength 193 nm) leads to the best results. For the diffractive marking of industrial glasses, a micrometer fine surface relief grating is machined into the glass surface filling the interior of a given macroscopic contour. Similar to holographic safety features on bank notes, processed areas appear in all spectral color upon directed illumination from the side. The laser marking works without weakening the glass matrix and the markings are reliably recognized by machine vision. A wide variety of markings in the forms of logos, texts, or codes can be realized, on plane or curved surfaces.
Further Information:
J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann
Effiziente diffraktive Markierung von Glasoberflächen mittels ArF-Excimerlaser
DGaO-Proceedings P30 (2019)
https://www.dgao-proceedings.de/download/120/120_p30.pdf
J. Meinertz, A. Gödecke , L.J. Richter, J. Ihlemann
Fast fabrication of diffractive patterns on glass by excimer laser ablation
Optics and Laser Technology 152, 108148 (2022)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S003039922200305X
Functional surfaces
Nanostructures have a great potential to generate special surface functionalities, without changing other material properties of the workpiece.
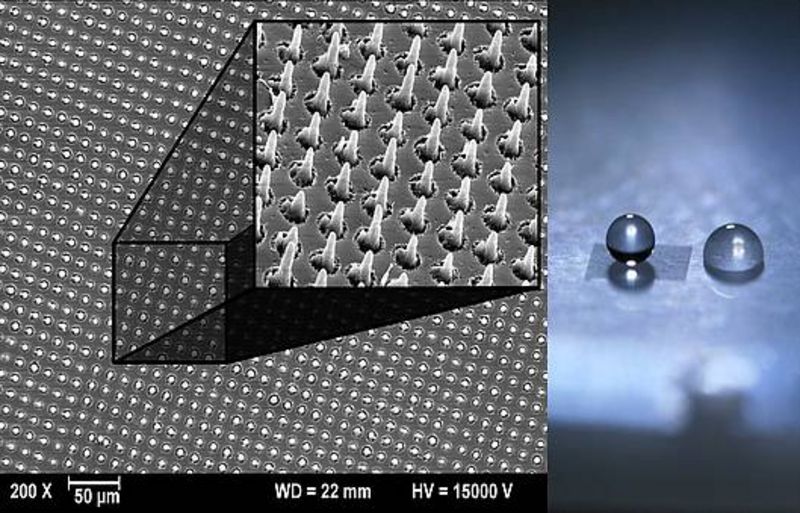
Generation of superhydrophobic surfaces with ultrashort laser pulses.
In case of certain materials (e.g. Polypropylene), micro- and nano- surface structures can change the wettability properties of the surface from neutral into superhydrophobic (so called “Lotus-effect”). Traditional methods of fabricating such surfaces are based either on chemical etching or special coating processes. However, low cost replication processes are mostly not supported. In cooperation with several partners, a new method was developed at LLG to fabricate micro-structured molds, capable to transfer the special properties into plastic surfaces. Maintaining a high durability necessitates the use of tough materials like tool-steel. Such materials with usually high thermal conductivity can only be sufficiently machined in the micro- and submicrometer range by applying ultrashort laser pulses. Highly efficient diffractive phase masks ensure the optimal use of the available laser energy. Such diffractive optics can efficiently be machined using special LLG-based technologies (Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 4, Appl. Phys A101, 225 (2010)). Such phase masks are optimal for fast and highly efficient laser processing of metallic stamps. In a subsequent process step, replicas of the processed stamp are produced by injection moulding, enabling the mass production of the surface patterns on plastics parts. The resulting topography facilitates a super-hydrophobic behavior of the fabricated components.
Surface Functionalization of Medicinal Stainless Steel
In modern medicine a numerous range of medicinal implants is used, including those not staying in the body permanently. Often, the ingrowth of an implant is unwanted, especially in the treatment of bone fractures by means of trauma implants or for intramedullary rods. Therefore, options are searched for to modify the implant surface such that the bone cell adhesion is impeded and thus the ingrowth is reduced. A reduced cell adhesion on the implant’s surface promises fewer complications during surgery when removing the implant and in particular a reduced risk for nerve injury. Medicinal stainless steel is commonly used as a material for trauma implants or intramedullary rods. With the objective “Light as a Tool” in collaboration with the Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials (IFAM) of the Fraunhofer Society, different methods for surface functionalizing of medicinal stainless steel were applied and tested under the aspect of cell adhesion.
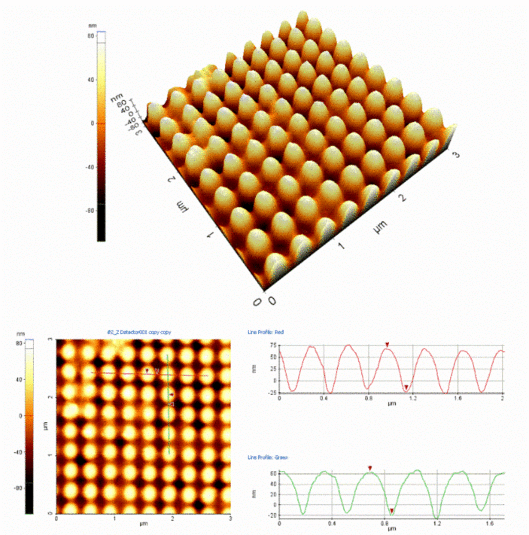
For this purpose, at the LLG ultrashort pulses were utilized for the contactless, topographic direct structuring of stainless steel surfaces. That way, periodic structures were produced on the sample surface with periods ranging from 0.5 µm-1.5 µm and a structural amplitude of approx. 200-1000 nm.
The samples were characterized by an atomic force microscope (AFM) and a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Afterwards they were treated with MG63 osteoblasts-like cells for biological testing through cell culture at IFAM. The influence of the patterns was evaluated optically with a fluorescence microscope. This revealed that all of the periodically structured areas of the samples showed a distinctly decreased surface coverage for the cells and a strongly reduced cell cross-linkage. Hence, it was shown that it is possible to induce a considerably reduced cell adhesion for implant surfaces through periodic structuring.

![]()

Micro-bumps on plastic surfaces fabricated via replication of laser machined moulds for the generation of super-hydrophobic surface wettability
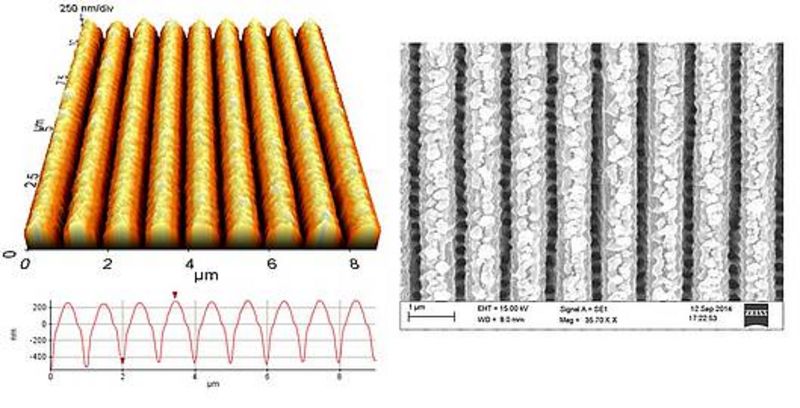
AFM- and SEM-picture of the structured area of the stainless steel sample with a period of 1.0 µm and a depth of approx. 800 nm
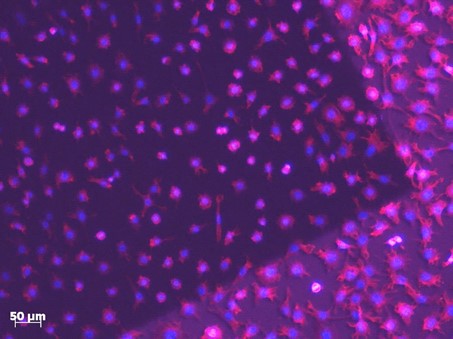
Picture taken with a fluorescence microscope of a stainless steel sample threated with MG63 osteoblasts-like cells (cytoskeleton dyed with Alexa-568 Phalloidin, nucleus with DAPI); the structured area is the darker one where fewer cells/cell cross-linkage are found. Picture provided by Dr. Ingo Grunwald, Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM
Phase controlled multiple beam interference
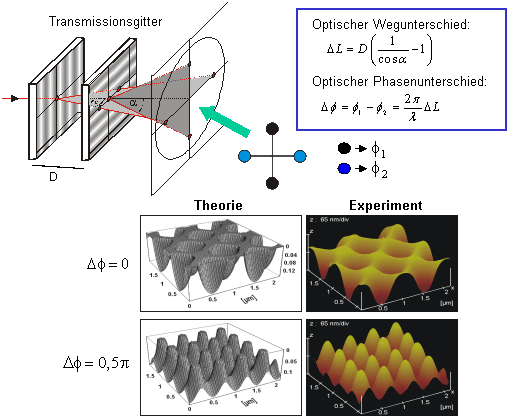
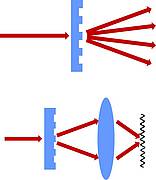
For the fabrication of periodic nanostructures it is straightforward to apply interferometric processing techniques. According to this approach a laser beam is subdivided into partial beams which are then recombined on the sample surface by means of an appropriate optical system. Applying a high enough intensity, the resulting interference pattern leads to a spatially periodic material ablation. The shape of the intensity distribution can be controlled by the intersection angle, the relative intensities, the polarization and also the phase relationship of the partial beams.
We introduced a scheme, the so called phase controlled multiple beam interference, which provides an easy means to change the relative phases of the interfering beams, thus allowing the fabrication of a great variety of complex structures.
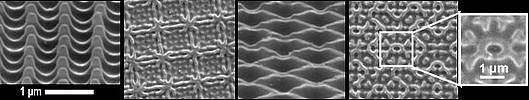
Complex suface structures fabricated by phase controlled multiple beam interference
Sub-wavelength pattern generation by laser direct writing
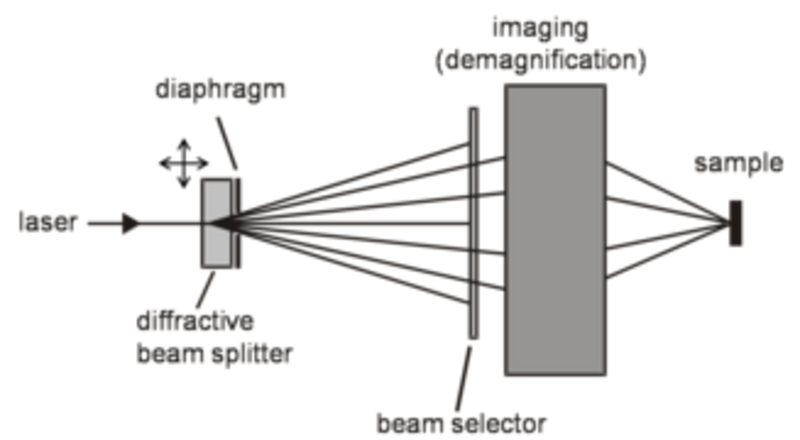
Sub-micron size periodic structures on surfaces of technologically important materials are known to give rise to new functionalities including field amplification, self-cleaning, holographic appearance, etc., thus opening up a row of novel applications. Special design of the topology can enhance a specific functionality and even multifunctional behavior can be realized. There is a general trend to reduce the size and increase the density of sub-micron features, demanding for the development of new fabrication technologies. Direct laser writing provides a very cheap, fast and flexible means for surface modification. In previous studies we could demonstrate the fabrication of high definition periodic structures by direct laser ablation, using a combination of multiple beam interference and mask projection. However, in such a scheme the achievable pattern density is limited by the numerical aperture of the applied optics and by diffraction, so that the minimum achievable period so far was limited to ~ 1.5 times the applied wavelength. Recently, we proposed a new way to overcome this limitation. The basic idea is to reduce the feature size of the periodic pattern by fluence control and increase the pattern density via repeated irradiation, as explained below.
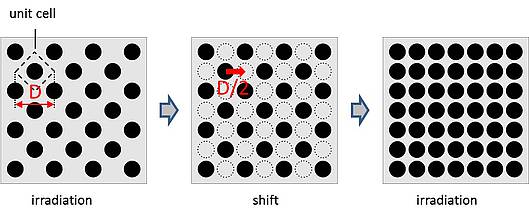
In every strictly periodic surface structure a ‘unit cell’ can be identified, whose topography is repeated along a one or two dimensional lattice. In the simplest case the unit cell (having a diagonal length of D) contains only one single feature. Our novel technique incorporates three steps: 1) apply laser patterning with an interference scheme, 2) shift the periodic pattern by D/2 (or in general an amount which is less than the size of the unit cell), and 3) repeat the laser patterning. As a result, we obtain a pattern with an increased density. The demagnification, which is inherent to our particular scheme, carries the potential of performing tiny lateral shifts of the projected pattern with extremely high accuracy. Thus, instead of translating the work piece between the subsequent irradiation cycles, the diffractive beam splitter is shifted laterally. This introduces a lateral displacement of the resulting diffraction pattern which experiences a strong demagnification in the plane of the work piece. Consequently, translation of a component in the micrometer range, which is easy to control, converts to a displacement of the illumination pattern on the work piece of the order of 100 nm.
For a feasibility test of the presented technique polyethylene sulfone (PES) samples were irradiated by 500 fs long laser pulses at a wavelength of 248 nm. By reducing the peak fluence from 500 mJ/cm2 down to 50 mJ/cm2 the individual feature sizes could be significantly reduced. After translating the diffraction pattern, the irradiation was repeated for a second time resulting in a topology with a doubled density.
Products and services
We offer customized UV femtosecond laser systems, special hollow fiber assemblies for pulse compression, phase/dielectric masks and feasibility studies for micro/nano-structuring solutions.
Contact us!
We are looking forward to developing tailored solutions for your problems.
Contact person:
Head of the Department
Dr. Peter Simon
“Short Pulses / Nanostructures”
Tel.: +49(0)551/5035-21
FAX: +49(0)551/5035-99
peter.simon@ifnano.de
Contact person for
Nano Structure Technology:
Dr. Jürgen Ihlemann
Tel.: +49(0)551/5035-44
Fax: +49(0)551/5035-99
juergen.ihlemann@ifnano.de
Stretched flexible hollow fiber for pulse compression
The standard way of compressing high power laser pulses down to durations in the few-cycle regime is to utilize spectral broadening in gas-filled hollow waveguides. According to recent technologies, the length of such fibres was limited to ~ 1 m. This posed a limitation to the achievable spectral broadening and hence the corresponding pulse compression capability, the transmission, and maximum energy throughput of these schemes.
HCF-IFNANO
We introduced a hollow fiber assembly incorporating a stretched flexible capillary, showing ideal waveguide properties at arbitrary lengths. Consequently, an essential former limitation ceased to apply. Therefore, the design strategy for the optimal fiber parameters can now be reformulated. As a result, with the new design, a record compression factor could be achieved. Moreover, compression of CEP stabilized pulses at 1 kHz was demonstrated down to ~3.5 fs with an energy of ~3.5 mJ, thus reaching a peak power of 1 TW. As a further record, our technology helped generating a train of 10 fs pulses, carrying 3.2 mJ at a repetition rate of 100 kHz, delivering an average power of over 300 W.
Available inner diameters 250 µm – 700 µm
Available fiber lenghts 0.3 m – 8 m
Phase masks and dielectric masks
Phase masks affect only the phase and not the amplitude of the transmitted light. Thus they offer low-loss operation compared to amplitude masks. Customized UV-transparent phase masks from SiO2are fabricated by laser ablation according to a patented process. Especially masks with medium feature sizes ranging from 10 µm to a few 100 µm are ideally producible with this method. They can be used e.g. as diffractive beam splitters or projection masks for demagnifying imaging. The phase masks are optimized for the specific application wavelength, which can be in the range from the deep UV to the near infrared.
Feasibility studies for surface nanostructuring
Laser micromachining: Feasibility studies
The IFNANO offers consulting and feasibility studies in the field of laser micromachining, including trials, manufacturing of samples, or small series production.
Typical applications:
• MEMS and microfluidic components
• Hole arrays
• Jet nozzles and micro channels
• Micro marking and diffractive marking
• Smoothing, roughening, functionalization of surfaces
• Micro optic components (micro lenses, masks, diffractive elements)
Publications
Publications
- L. J. Richter, U. Ross, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Transmission electron microscopy analysis of UV laser implanted gold nanoparticles and their influence on photoluminescence enhancement from silicon nanocrystals, Discover Nano 20, 82 (2025)
Publications
- N. Bakhtiari, J.Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Fluidic Submicron-Channels by Pulsed Laser-Induced Buckling of SiOx Films on Fused Silica
Discover Nano 19, 46 (2024)
Conference Contributions
- N. Bakhtiari, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Nanofluidic Channels by Pulsed Laser Irradiation of SiOx-coated Fused Silica
CINSaT Spring Colloquium, Paderborn (03.2024) - N. Bakhtiari, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Nanofluidic Channels by Pulsed Laser Irradiation of SiOx-coated Fused Silica
DPG Frühjahrstagung, Fachverband Oberflächenphysik, Berlin (03.2024) - L. J. Richter, C. M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Erzeugung schwarzer Markierungen durch UV-Laser Bestrahlung von TiO2-haltigen
handelsüblichen Gläsern, Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik (DGaO) Aachen (05.2024) - J. Ihlemann, N. Bakhtiari, J. Meinertz, L. J. Richter:
Laser precision microfabrication of optical and fluidic components on the basis of silicon suboxide thin films
25th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM2024), San Sebastian, Spain (05.2024) - Hendrik M. Wrigge, Pascal D. Ndione, Bärbel Rethfeld, Peter Simon
Broadband pump probe setup for ultrafast transient reflectivity measurements
COLA 2024, 17th International Conference on Laser Ablation Hersonissos, Crete, Greece (09.2024) - A. Röben, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Laserbasierte Spannungskompensation bei Glassubstraten in der Dünnschichttechnologie
F.O.M-Konferenz „GEMEINSAMER FORTSCHRITT DURCH IGF-FORSCHUNG IN OPTIK, PHOTONIK, ANALYSEN- UND MEDIZINTECHNIK“
Berlin (11.2024)
Publications
- L. Fütterer, C.M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Viscoelastic deformation of borosilicate glass substrates induced by a laser-patterned silicon suboxide film
Applied Physics A 129, 107 (2023) - L.J. Richter, U. Ross, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Excimer laser surface patterning for photoluminescence enhancement of silicon nanocrystals
Photonics 10, 358 (2023) - J. Meinertz, L.J. Richter, C.M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Precision marking of glass with excimer lasers
PhotonicsViews 2/2023, p. 62 - J. Ihlemann, A. Blumenstein, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
Periodic Surface Structures by Laser Interference Ablation
in: Ultrafast Laser Nanostructuring – The Pursuit of Extreme Scales, Razvan Stoian, Jörn Bonse eds.
Springer Series in Optical Sciences 239, 495 (2023) - J. Meinertz, L.J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Phase masks for laser interference processing
IVAM Hightech-Magazin ››inno‹‹ – Photonics – The Power of Light 84, 4 (2023)
Publications
- P. N. Terekhin, J. Oltmanns, A. Blumenstein, D. S. Ivanov, F. Kleinwort, M. E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann and P. Simon:
Key role of surface plasmon polaritons in generation of periodic surface structures following single-pulse laser irradiation of a gold step edge
Nanophotonics 11(2), 359–367 (2022) - C. M. Beckmann, L. J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Freeform shaping of fused silica substrates via viscous deformation induced by a laser patterned, stressed film
Optics Express 30, 6726 (2022) - J. Meinertz, A. Gödecke, L.J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Fast fabrication of diffractive patterns on glass by excimer laser ablation
Optics and Laser Technology 152, 108148 (2022) - J. Ihlemann, L. J. Richter, J. Meinertz, J. Wunderlich, N. Schindler, A. Günther, B. Oberleiter, T. Rainer:
Glass marking by laser transfer implantation (LTI) of plasmonic nanoparticles
Optics and Laser Technology 155, 108371 (2022) - L. J. Richter, C .M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
UV laser generated micro structured black surface on commercial TiO2-containing glass
Applied Surface Science 601, 154231 (2022) - L. J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Photoluminescence enhancement of silicon nanocrystals by excimer laser implanted gold nanoparticles
Applied Physics A 128, 764 (2022) - M. Edakubo, L. J. Richter, Y. Haraguchi, H. Aruga-Katori, J. Ihlemann, G. Miyaji:
Improvement of optical transmittance of SiO2 surface by femtosecond-laser-induced homogeneous nanostructure formation
Optical Materials Express 12, 3982 (2022)
Conference constributions
- L. J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Laser based methods for photoluminescence enhancement of silicon nanocrystals
16th International Conference on Laser Ablation COLA 2021/22
Matsue, Japan (04.2022) - M.Edakubo, Y. Haraguchi, H. Aruga-Katori, G. Miyaji, L.J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Homogeneous Nanostructures on SiO2 formed with Femtosecond Laser Pulses and Improvement of Optical Transmittance
16th International Conference on Laser Ablation COLA 2021/22
Matsue, Japan (04.2022) - P. N. Terekhin, J. Oltmanns, D.S. Ivanov, F. Kleinwort, M.E. Garcia, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon, B. Rethfeld:
Role of Surface Plasmon Polaritons in Nanophotonics and Nanostructuring
CLEO: Applications and Technology 2022
San Jose, USA (05.2022) - A. Röben, C. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Stress based figure correction and surface-metrology of optical substrates
Humboldt meets Leibniz – Emerging Topics in Optics and Photonics
Hannover (06.2022) - J. Ihlemann, L.J. Richter, C.M. Beckmann, J. Meinertz:
High resolution UV laser marking of glass surfaces
The 23rd International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication – LPM2022
Dresden (06.2022) - C. M. Beckmann, L. Fütterer, L. J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Freeform shaping of silicate glass substrates via a viscous deformation and a laser patterned, stressed film
26th International Congress on Glass (ICG)
Berlin (07.2022) - J. Ihlemann, L. J. Richter, C. M. Beckmann, J. Meinertz:
High resolution UV laser marking of glass surfaces
26th International Congress on Glass (ICG)
Berlin (07.2022) - A. Röben, C. M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Formkorrektur von Glassubstraten in der Dünnschichttechnologie
mittels ArF-Excimer-Laser Bestrahlung
Arbeitskreistreffen des PhotonicNet-AK DUV/VUV-Optik
Alzenau (10.2022) - J. Ihlemann, L. J. Richter, C. M. Beckmann, J. Meinertz:
Laser based fabrication of photonic nanostructures and nanoparticlesCINSaT autumn colloquium
Kassel (11.2022) - C. M. Beckmann, A. Röben, J. Ihlemann:
Laserbasierte Spannungskompensation bei Glassubstraten in der Dünnschichttechnologie
F.O.M.-Konferenz 2022: Gemeinsamer Fortschritt durch IGF-Vorlaufforschung in Optik, Photonik und Medizintechnik
Berlin (11.2022) - J. Meinertz, L. J. Richter, C. M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laserbasierte Markierung von Glasoberflächen
Workshop Laserbearbeitung von Glaswerkstoffen
Nürnberg (12.2022)
Publications
- L. J. Richter, C. Beckmann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Fused Silica Phase Masks Enhance Laser Processing and Microscopy
Photonics Spectra, July 2021, p. 56-61 - P. Simon, J. Ihlemann, J. Bonse:
Editorial: Special Issue “Laser-Generated Periodic Nanostructures”
Nanomaterials 11, 2054 (2021) - J. Oltmanns, P.N. Terekhin, F. Kleinwort, A. Blumenstein, D.S. Ivanov, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Influence of the Laser Beam Shape on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure Formation Assisted by Surface Plasmon Polaritons,JLMN-Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 16 (3), 199 (2021)
Conference constributions
- Shestaev, S. Hädrich, N. Walter, T. Nagy, P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, A. Klenke, R. Klas, J. Buldt, H. Stark, M. Gebhardt, S. Breitkopf, C. Gaida, P. Jójárt, I. Seres, Z. Várallyay, Á. Börzsönyi, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
CEO-stable pulses from a 1kW fiber CPA
Proceedings Volume 11676, Frontiers in Ultrafast Optics: Biomedical, Scientific,
and Industrial Applications XXI; 116760K (2021) https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2577617,
Event: SPIE LASE, 2021, Paper 11676-16 Virtual (03.2021) - P.N. Terekhin, J. Oltmanns, A. Blumenstein, D.S. Ivanov, F. Kleinwort, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Design of periodic structures by surface plasmon polaritons excitation,
DPG-Spring meeting on Surface Science, Virtual (03.2021) - J. Oltmanns, P.N. Terekhin, D.S. Ivanov, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Investigation of the plasmonic nature of laser-induced periodic surface structures,
The 22nd International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM 2021), Virtual (06.2021) - L. Fütterer, C. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Viscoelastic deformation of glass substrates by laser patterned stressed films,
DPG-Workshop Applied photonics, Bad Honnef (09.2021) - L. J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Laser-based methods for luminescence enhancement of Si-nanocrystals by coupling to plasmonic nanoparticles,
DPG-Workshop Applied photonics, Bad Honnef (09.2021) - P.N. Terekhin, F. Kleinwort, J. Oltmanns, A. Blumenstein, D.S. Ivanov, M.E. Garcia, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon, B. Rethfeld:
Evidence of plasmonic nature of self-arranged surface nanostructuring after single femtosecond laser pulse irradiation,
DPG-Workshop Applied photonics, Bad Honnef (09.2021)
Publications
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
Laser interference ablation by ultrashort UV laser pulses via diffractive beam management
Advanced Optical Technologies 9, 41 (2020) - J. Meinertz, L.J. Richter, C.M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Quarzphasenmasken für Mikroskopie und Lasermaterialbearbeitung
Photonik 1.2020, p. 49 - A. Blumenstein, E.S. Zijlstra, D.S. Ivanov, S.T. Weber, T. Zier, F. Kleinwort, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon, M.E. Garcia:
Transient optics of gold during laser irradiation: from first principles to experiment
Physical Review B 101, 165140 (2020) - C.M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Figure correction of borosilicate glass substrates by nanosecond UV excimer laser irradiation
Optics Express 28, 18681 (2020) - Avakyan, V. Durimanov, D. Nemesh, V. Srabionyan, J. Ihlemann, L. Bugaev:
Theoretical approach for calculation of dielectric functions of plasmonic nanoparticles of noble metals, magnesium and their alloys
Optical Materials 109, 110264 (2020) - Takaya, G. Miyaji, I. Takahashi, L.J. Richter, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of periodic nanostructures on silicon suboxide films with plasmonic near-field ablation induced by low-fluence femtosecond laser pulses
Nanomaterials 10, 1495 (2020) - A. Blumenstein, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann, D.S. Ivanov:
Formation of periodic nanoridge patterns by ultrashort single pulse UV laser irradiation of gold
Nanomaterials 10, 1998 (2020) - M. Ouillé, A. Vernier, F. Böhle, M. Bocoum, A. Jullien, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, Z. Cheng, D. Gustas, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, S. Haessler, J. Faure, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic-intensity near-single-cycle light waveforms at kHz repetition rate
Light Sci Appl 9, 47 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0280-5 - K. Oliver Böker, F. Kleinwort, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon, K. Jäckle, S. Taheri, W. Lehmann, A. F. Schilling:
Laser Ablated Periodic Nanostructures on Titanium and Steel Implants Influence Adhesion and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem
CellsMaterials 2020 13, 3526; doi:10.3390/ma13163526 - T. Nagy, P. Simon, L. Veisz:
High-energy few-cycle pulses: post-compression techniques
Advances in Physics: X, 6:1, 1845795, DOI: 10.1080/23746149.2020.1845795
Conference contributions
- C. M. Beckmann, J. Ihlemann:
Figure correction of borosilicate glass substrates by nanosecond UV-laser irradiation
21st International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM)
Virtual (06.20) - P. Simon, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, A. Blumenstein, J. Ihlemann:
Interference ablation by ultrashort laser pulses via diffractive beam management
21st International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM)
Invited talk, Virtual (06.20) - J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, M. Heinz, T. Fricke-Begemann, M. Dubiel
UV laser micro processing of doped glass
21st International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM)
Virtual (06.20) - S. Hädrich, N. Walther, E. Shestaev, T. Nagy, P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, R. Klas, J. Buldt, H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, I. Seres, Z. Várallyay, Á. Börzsönyi, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
High Pulse Energy CEP-stable Few-cycle Pulses at High Average Power: Status of the ELI-ALPS HR2 System
High-brightness Sources and Light-driven Interactions Congress, HILAS, OSA Virtual Event, paper HTh3B.2 (11.20) - T. Nagy, S. Hädrich, P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, N. Walther, R. Klas, J. Buldt, H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, I. Seres, Z. Várallyay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
Pulse compression to 3-cycle duration beyond 300 W average power
Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, CLEO 2020, invited paper SM2H. - S. Hädrich, N. Walther, M. Kienel, P. Simon, T. Nagy, A. Blumenstein, E. Shestaev, R. Klas, J. Buldt, L.-H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, Z. Várallyay, K. Osvay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
500W, 5mJ, 6fs, CEP-stable few-cycle pulses. An update on the ELI-ALPS HR2 beamline
Fiber Lasers XVII: Technology and Systems, San Francisco, USA, (Invited Talk, Paper 11260-7) (02.20)
Publications
- V.V. Srabionyan, M. Heinz, S.Y. Kaptelinin, L.A. Avakyan, G.B. Sukharina, A.V. Skidanenko, V.V. Pryadchenko, K.G. Abdulvakhidov, A.S. Mikheykin, V.A. Durymanov, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann,
M. Dubiel, L.A. Bugaev:
Effect of thermal post-treatment on surface plasmon resonance characteristics of gold nanoparticles formed in glass by UV laser irradiation,
Journal of Alloys and Compounds 803, 354 (2019) - L. J. Richter, C. Beckmann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Multilevel Fused Silica Diffractive Phase Elements by Laser Processing of Silicon Suboxide,
DGaO-Proceedings A32 (2019)
- J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Effiziente diffraktive Markierung von Glasoberflächen mittels ArF-Excimerlaser,
DGaO-Proceedings P30 (2019) - J.-H. Klein-Wiele, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
Complex diffractive surface patterns on metals by UV-ps laser ablation,
Optics Express 27, 28902 (2019) - S. Rung, K. Bokan, F. Kleinwort, S. Schwarz, P. Simon, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, C. Esen, R. Hellmann:
“Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods”,
Lubricants 7, 43 (2019) - N. G. Khodakovskiy, M. P. Kalashnikov, V. Pajer, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, M. M. Toktamis, M. Lozano, B. Mercier, Z. Cheng, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
“Generation of few-cycle laser pulses with high temporal contrast via nonlinear elliptical polarisation rotation in a hollow fibre compressor”,
Laser Phys. Lett. 16 095001 (2019) - T. Nagy, S. Hädrich, P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, N. Walther, R. Klas, J. Buldt, H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, I. Seres, Z. Várallyay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
Generation of three-cycle multi-millijoule laser pulses at 318 W average power,
Optica 6, 1423 (2019)
Conference constributions
- N. G. Khodakovskiy, M. P. Kalashnikov, B. Mercier, V. Pajer, Z. Cheng, M. Lozano, A. Blumenstein, P. Simon, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
“High-fidelity few-cycle laser pulses generated via nonlinear ellipse rotation”, Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC 2019, Münich, Germany, 23-27 June 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CLEOE-EQEC.2019.8873203, (poster, CF-P40 SUN) - S. Hädrich, P. Simon, T. Nagy, A. Blumenstein, R. Klas, J. Buldt, L.-H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, Z. Várallyay, K. Osvay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
“Spectral Broadening of a 500W, 5mJ Femtosecond Laser”, Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) 2019, DOI: 10.1109/CLEOE-EQEC.2019.8873189 - J. Ihlemann, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, J. Oltmanns, D.S. Ivanov, P.N.Terekhin, B. Rethfeld, M. E. Garcia, P. Simon:
Generation of deterministic nanostructures with ultrashort UV pulses under predefined interface boundary conditions,
W05,06-2, INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM: FUNDAMENTALS OF LASER ASSISTED MICRO-&NANOTECHNOLOGIES, FLAMN 2019, Saint-Petersburg, Russia - S. Hädrich, P. Simon, T. Nagy, A. Blumenstein, R. Klas, J. Buldt, L.-H. Stark, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, Z. Várallyay, K. Osvay, T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
“Spectral Broadening of a 500W, 5mJ Femtosecond Laser”, 7th International Conference on Attosecond Science and Technology, Atto 2019, Szeged, Hungary - A. Blumenstein, D.S. Ivanov, E.S. Zijlstra, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Gold Surface Nanostructuring with Ultrashort Laser Pulses – Study of Non-equilibrium Effects, FemtoMat 2019, Femtomat, March 18–20, 2019, Mauterndorf Castle, Mauterndorf, Salzburg, Austria - S. Hädrich, P. Simon, T. Nagy, A. Blumenstein, N. Walther, M. Kienel, E.Shestaev, F. Stutzki, C. Gaida, S. Breitkopf, P. Jójárt, Z. Várallyay, K. Osvay, T. Eida, J. Limpert:
3.2-mJ sub-10-fs pulses at 100 kHz Advanced Solid State Laser Conference 2019, Vienna, Austria, 29 September- 3 October 2019, (postdeadline talk, ATu6A.2) - S. Breitkopf, S. Hädrich, M. Kienel, P. Jójárt, Z. Várallyay, K. Osvay, .P. Simon, T. Nagy, A. Blumenstein, R. Klas, J. Buldt, L.-H. Stark, E. Shestaev , T. Eidam, J. Limpert:
Yb-doped fiber laser system with 1kW, 10mJ and <300fs pulse for the generation of TW class few-cycle pulses, Ultrafast Optics XII 2019, Bol, Croatia, 6-11 October 2019, (regular talk, TU8.4)
Publications
- M. Heinz, V.V. Srabionyan, L.A. Avakyan, A.L. Bugaev,
A.V. Skidanenko, V.V. Pryadchenko, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, C. Patzig, M. Dubiel, L.A. Bugaev:
Formation and implantation of gold nanoparticles by ArF-excimer laser irradiation of gold-coated float glass,
Journal of Alloys and Compounds 736, 152 (2018)
- L. Avakyan, M. Heinz, A. Skidanenko, K.A. Yablunovskiy, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, C. Patzig, M. Dubiel, L. Bugaev:
Insight on agglomerates of gold nanoparticles in glass based on surface plasmon resonance spectrum: Study by multi-spheres T‑matrix method,
Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 30, 045901 (2018)
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
Formation of porous silicon oxide from substrate-bound silicon rich silicon oxide layers by continuous-wave laser irradiation,
Journal of Applied Physics 123, 093104 (2018)
- M. Heinz, V.V. Srabionyan, L.A. Avakyan, A.L. Bugaev, A.V. Skidanenko, S.Yu. Kaptelinin, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, C. Patzig, M. Dubiel, L.A. Bugaev:
Formation of bimetallic gold-silver nanoparticles in glass by UV laser irradiation,
Journal of Alloys and Compounds 767, 1253 (2018)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Hybrid micro-optical elements by laser-based fabrication of Fresnel lenses on the end face of gradient index lenses,
Optics Express 26, 23751 (2018) - L.J. Richter, C.M. Beckmann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Laser Processing of Silicon Suboxide for the Fabrication of Multilevel Fused SilicaDiffractive Phase Elements,
JLMN-Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 13, 249 (2018) - M. Heinz, J. Meinertz, M. Dubiel, J. Ihlemann:
Excimer laser induced spatially resolved formation and implantation of plasmonic particles in glass,
Nanomaterials 8, 1035 (2018)
Conference constributions
- L.J. Richter, C. Beckmann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Laser processing of silicon suboxide for the fabrication of diffractive phase elements,
DPG Frühjahrstagung, Fachverband Kurzzeit- und angewandte Laserphysik
Erlangen (03.2018) - J. Ihlemann:
Laser processing of silicon suboxide (SiOx) – from the generation of Si-nanocrystals to the fabrication of diffractive phase elements,
International Workshop on Frontiers in Lasers and Applications (FLA 2018)
Okinawa, Japan (04.2018) - L.J. Richter, C.M. Beckmann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann
Laser processing of silicon suboxide for the fabrication of multilevel fused silica diffractive phase elements,
19th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM 2018)
Edinburgh, UK (06.2018)
Publications
- L. Shi, B. Iwan, R. Nicolas, Q. Ripault, J.R.C. Andrade, S. Han, H. Kim, W. Boutu, D. Franz,
T. Heidenblut, C. Reinhardt, B. Bastiaens, T. Nagy, I. Babushkin, U. Morgner, S. Kim,
G. Steinmeyer, H. Merdji, M. Kovacev:
Self-optimization of plasmonic nanoantennas in strong femtosecond fields, Optica 4, 1038-1043 (2017)
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, K. Thiel, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
Microstructural analysis of the modifications in substrate-bound silicon-rich silicon oxide induced by continuous wave laser irradiation,Journal of Alloys and Compounds 707, 227 (2017)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, A. Hoell:
Investigation of gold and bimetallic gold/silver nanoparticles in soda-lime-silicate glasses formed by means of excimer laser irradiation, Proc. SPIE 10093, 100930I (2017)
- D. S. Ivanov, A. Blumenstein, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon, M. E. Garcia,·B. Rethfeld:
Molecular dynamics modeling of periodic nanostructuring of metals with a short UV laser pulse under spatial confinement by a water layer, Applied Physics A 123, 744 (2017)
Conference constributions
- P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, J. Ihlemann, B. Rethfeld, D.S. Ivanov, M. E. Garcia:
Nano-structure formation on gold and silicon surfaces by laser irradiation, FemtoMat 2017, Mauterndorf, Austria March 2017 (invited talk) - A. Blumenstein, D.S. Ivanov, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
Nano ridge formation by ultrashort UV laser irradiation of gold International Conference on Laser Ablation (COLA), Marseille (09.2017) - J. Meinertz, R. Karstens, H. Stark, J. Ihlemann:
Periodic patterning of glass by phase mask projection International Conference on Laser Ablation (COLA), Marseille (09.2017) - T. Fricke-Begemann, K. Rewerts, N. Wang, P. Peretzki, C. Gobert, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Laser annealing of SiOx films for the generation of luminescent silicon nanoclusters and nanocrystals International Conference on Laser Ablation (COLA), Marseille (09.2017) - J. Ihlemann: DUV/VUV-Laser-Mikrobearbeitung transparenter Materialien PhotonicNet Arbeitskreistreffen DUV-VUV Göttingen (11.2017) J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser-Mikro- und Nanostrukturierung von Glas Workshop Laserbearbeitung von Glaswerkstoffen, Nürnberg (12.2017)
- D. Tasche, C. Gerhard, J. Ihlemann, W. Viöl:
Einfluss des Wasserstoffgehaltes und Stöchiometrieverhältnisses von O und Si auf die Excimerlaserablation von Quarzglas,
18. Fachtagung für Plasmatechnologie PT-18, Göttingen (02.2017)
- C. Gobert, N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
Micro-Raman spectroscopy of laser-annealed reheated SiOxfilms on silica substrate,
DPG-Frühjahrstagung, Dresden (03.2017)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, L. Avakyan, A. Bugaev, L. Bugaev, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz:
ArF-excimer laser irradiation of gold coated float glass – formation and implantation of gold nanoparticles,
DPG-Frühjahrstagung, Dresden (03.2017)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, A. Hoell:
Investigation of gold and bimetallic gold/silver nanoparticles in soda-lime-silicate glasses formed by means of excimer laser irradiation, Synthesis and Photonics of Nanoscale Materials XIV, Photonics West San Francisco (01.2017)
- D.S. Ivanov, A. Blumenstein, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Theoretical investigation of periodic nanostructuring mechanism of Au due to UV laser pulse with and without spatial confinement, E-MRS, Spring meeting Strasbourg (05.2017)
- J. Ihlemann:
Micro- and Nanopatterning of Surfaces by Short and Ultrashort UV Laser Pulses PhotonicNet-Symposium: Surface Processing,
Göttingen (06.2017)
- F. Boehle, A. Blumenstein, A. Vernier, A. Jullien, M. Kretschmar, M. Kovacs, R. Romero, H. Crespo,
P. Simon, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic-intensity near-single-cycle pulses from a stretched hollow-fiber compressor at 1kHz, SPIE Optics & Optoelectronics 2017, Prague-Czech Republic, 24-27 April 2017
- F. Boehle, A. Blumenstein, M. Bocoum, A. Vernier, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, A. Jullien, D. Gustas,
D. Guénot, J. Faure, M. Kovacs, M. Kretschmar, P. Simon, U. Morgner, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic-intensity 1.3 optical cycle laser pulses at 1kHz from a stretched hollow-fiber compressor,
CLEO/QELS 2017, San Jose (CA) USA, 14-19 May 2017
- F. Boehle, A. Blumenstein, M. Bocoum, A. Vernier, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, A. Jullien, D. Gustas,
D. Guénot , J. Faure , M. Kretschmar, P. Simon , T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic plasma mirrors at 1kHz, TARG3: Targetry for high repetition rate laser-driven sources,
Salamanca-Spain, 21-23 June 2017
- F. Böhle, M. Bocoum, A. Vernier, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, A. Jullien, D. Gustas, D. Guénot,
J. Faure, M. Kovacs, M. Kretschmar, P. Simon, U. Morgner, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic-Intensity 1.3 Optical Cycle Laser Pulses at 1kHz from a Stretched Hollow-Core-Fiber Compressor,
CLEO Europe 2017, Munich-Germany, 25-29 June 2017
- F. Boehle, A. Blumenstein, M. Bocoum, A. Vernier, M. Lozano, J.-P. Rousseau, A. Jullien, D. Gustas,
D. Guénot, J. Faure, M. Kovacs, M. Kretschmar, P. Simon, U. Morgner, T. Nagy, R. Lopez-Martens:
Relativistic-intensity near-single-cycle laser pulses at 1kHz, Ultrafast Optics XI, Jackson Hole (WY) USA, 8-13 October 2017 - P. Simon, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, J. Ihlemann, B. Rethfeld, D.S. Ivanov, M. e. Garcia: “Nano-structure formation on gold and silicon surfaces by laser irradiation”, FemtoMat 2017, Mauterndorf, Austria, March 2017 (invited talk)
Publications
- A. B. Borisov, J. C. McCorkindale, S. Poopalasingam, J. W. Longworth, P. Simon, S. Szatmári,
C. K. Rhodes:
Rewriting the rules governing high intensity interactions of light with matter,
Rep. Prog. Phys. 79 046401 (2016)
- H. Stolzenburg, P. Peretzki, N. Wang, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Implantation of plasmonic nanoparticles in SiO2 by pulsed laser irradiation of gold films on SiOx-coated fused silica and subsequent thermal annealing,
Applied Surface Science 374, 138 (2016)
- R. Karstens, A. Gödecke, A. Prießner, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of 250-nm-hole arrays in glass and fused silica by UV laser ablation,
Optics and Laser Technology 83, 16 (2016)
- M. Heinz, V.V. Srabionyan, A.L. Bugaev, V.V. Pryadchenko, E.V. Ishenko, L.A. Avakyan,
Y.V. Zubavichus, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, E. Pippel, M. Dubiel, L.A. Bugaev:
Formation of silver nanoparticles in silicate glass using excimer laser radiation: structural characterization by HRTEM, XRD, EXAFS and optical absorption spectra,
Journal of Alloys and Compounds 681, 307 (2016)
- A. Tajalli, B. Chanteau, M. Kretschmar, H.G. Kurz, D. Zuber, M. Kovačev, U. Morgner, T. Nagy:
Few-cycle optical pulse characterization via cross-polarized wave generation dispersion scan technique,
Optics Lett. 41, 5246 (2016)
- H.G. Kurz, M. Kretschmar, T. Binhammer, T. Nagy, D. Ristau, M. Lein, U. Morgner, M. Kovačev:
Revealing the Microscopic Real-Space Excursion of a Laser-Driven Electron, (see also “Supplementary Information”,
Rev. X 6, 031029 (2016)
- M. Dubiel, M. Heinz, V. V. Srabionyan, V. V. Pryadchenko, L. A. Avakyan, Ya. V. Zubavichus,
J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, L. A. Bugaev:
Silver nanoparticles in silicate glass prepared by UV laser: dependences of size and atomic structure of particles upon irradiation parameters, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 712, 012110 (2016)
- R. Karstens, A. Gödecke, A. Prießner, J. Ihlemann:
UV-laser fabrication of sub-micron hole arrays in glass by phase mask projection,
DGaO Proceedings (2016)
- D.S. Ivanov, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, M. E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon,
V. P. Veiko, E. Jakovlev:
“Molecular Dynamics Modeling of Periodic Nanostructuring of Au with a UV Short Laser Pulse at a High Fluence Regime”,
International Symposium Fundamentals of Laser Assisted Micro– and Nanotechnologies (FLAMN-16), St. Petersburg, 2016
Conference constributions
- A. Blumenstein, E.S. Zijlstra, D.S. Ivanov, M.E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Laser pulse reflectivity changes on gold at elevated electronic temperatures,
HPLA, Santa Fe (2016)
- D. Köhne, C. Geisler, P. Simon, A. Egner:
Principles and applications of optical switching assisted imaging and structuring schemes, International Conference on Physics June 2016, New Orleans, USA
- R. Karstens, A. Gödecke, A. Prießner, J. Ihlemann:
UV-laser fabrication of sub-micron hole arrays in glass by phase mask projection, 117. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik, Hannover (05.2016)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser Mikro- und Nanostrukturierung von Oberflächen,
PhotonicNet-Symposium: Funktionalisierte Oberflächen, Göttingen (06.2016)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, K. Rewerts, N. Wang, P. Peretzki, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Formation of silicon nanocrystals by continuous wave laser annealing of SiOx films,
10th International Conference on Photoexcited Processes and Applications (ICPEPA), Brasov (08-09.2016)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser Mikro- und Nanostrukturierung von Oberflächen und Schichten für optische Anwendungen,
Seminar Nanostrukturen für optische Komponenten, Aachen (09.2016)
- H.G. Kurz, M. Kretschmar, T. Binhammer, T. Nagy, D. Ristau, M. Lein, U. Morgner, M. Kovačev:
Probing the Electronic Excursion during High-Order Harmonic Generation,
High-Brightness Sources and Light-Driven Interactions HILAS, Long Beach, California, USA, HT2B.4 (2016)
- M. Kretschmar, C. Bree, T. Nagy, H. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovačev:
High-order harmonics as a nonlinear tool to track pulsedynamics along a filament, High-Brightness Sources and Light-Driven Interactions HILAS, Long Beach, California, USA, HS4B.5 (2016)
- A. Tajalli, B. Chanteau, M. Kretschmar, H. Kurz, M. Kovacev, U. Morgner, T. Nagy:
Few-cycle pulse characterization using XPW d-scan, High-Brightness Sources and Light-Driven Interactions HILAS,
Long Beach, California, USA, HS3B.5 (2016)
- A. Tajalli, B. Chanteau, M. Kretschmar, H. Kurz, M. Kovacev, U. Morgner, T. Nagy:
Full characterization of few-cycle pulses using cross-polarized wave generation d scan technique,
CLEO, San Jose, California, USA, FF1M.8 (2016)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele:
Zell-Adhäsions-Reduzierte Traumaimplantate, F.O.M.-Jahreskonferenz, Berlin 2016
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele:
Oberflächenfunktionalisierung zur Adhäsions-Reduzierung von humanen Zellen auf Traumaimplantaten, InnoPlanT-Netzwerktreffen – Thema “Implantatoberflächen”, Erlangen (20.10.2016)
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
The formation of nc-Si in SiOx induced by continuous-wave laser irradiation,
DPG-Frühjahrstagung, Regensburg (03.2016)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, V. Srabionyan, V. Pryadchenko, L. Avakyan, Y. Zubavichus, J. Meinertz,
J. Ihlemann, L. Bugaev:
Silver nanoparticles in silicate glass prepared by UV laser: correlations between the optical properties and the atomic structure of the silver nanoparticles, 90. Glastechnische Tagung Goslar (06.2016)
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, K. Rewerts, P. Peretzki, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
The formation of nanocrystaline Si in substrate bound silicon rich silicon oxide by damage free continuous wave laser irradiation, 23rd International Symposium on Metastable, Amorphous and Nanostructured Materials (ISMANAM 2016),
Nara, Japan (07.2016)
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, K. Thiel, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
The micro-structural analysis of damaged region in substrate-bound silicon-rich silicon oxide induced by continuous wave laser irradiation, 23rd International Symposium on Metastable, Amorphous and Nanostructured Materials (ISMANAM 2016)
Nara, Japan (07.2016)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, C. Dölle, L. Wittig, M. Brandmann, N. Suter, S. Dervis, F. Kleinwort, P. Simon,
I. Grunwald:
Oberflächenfunktionalisierung zur Adhäsions-Reduzierung von humanen Zellen auf Traumaimplantaten, 23. Innovationstag Mittelstand des BMWi, Berlin (2.6.2016)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, C. Dölle, L. Wittig, M. Brandmann, N. Suter, S. Dervis, F. Kleinwort, P. Simon,
I. Grunwald:
Oberflächenfunktionalisierung zur Adhäsions-Reduzierung von humanen Zellen auf Traumaimplantaten, F.O.M.-Jahreskonferenz,
Berlin (2016)
Publications
- D. Köhne, T. Fricke-Begemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Large area silica nano grids by homogeneous high resolution laser patterning of SiOx-films,
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 10, 158 (2015)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, N. Wang, P. Peretzki, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Generation of silicon nanocrystals by damage free continuous wave laser annealing of substrate-bound SiOxfilms,
Journal of Applied Physics 118, 124308 (2015)
- M. Hofmann, J. Hyyti, S. Birkholz, M. Bock, S.K. Das, R. Grunwald, M. Hoffmann, T. Nagy,
A. Demircan, M. Jupé, D. Ristau, U. Morgner, C. Brée, M. Woerner, T. Elsaesser, G. Steinmeyer:
Noninstantaneous polarization dynamics in dielectric media,
Optica 2, 151-157 (2015)
- C. Brée, M. Kretschmar, T. Nagy, H.G. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovačev:
Impact of spatial inhomogeneities on on-axis pulse reconstruction in femtosecond filaments,
J. Phys. B 48, 094002 (2015)
- D. S. Ivanov, V. P. Lipp, A. Blumenstein, F. Kleinwort, V. P. Veiko, E. Yakovlev, V. Roddatis, M. E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Experimental and theoretical investigation of periodic nanostructuring of Au with ultrashort UV laser pulses near the damage threshold,
Phys. Rev. Applied 4, 064006 (2015)
- J. Borisov, J. McCorkindale, S. Poopalasingam, J. Longworth, P. Simon, S. Szatmári, C.K. Rhodes:
Rewriting the rules governing high intensity interactions of light with matter: a review,
Reports on Progress in Physics, IOP Publishing, accepted 18 Mai 2015
Conference constributions
- J. Hyyti, M. Hofmann, S. Birkholz, M. Bock, S.K. Das, R. Grunwald, M. Hoffmann, T. Nagy, A. Demircan, M. Jupé, D. Ristau, U. Morgner, C. Brée, M. Woerner, T. Elsaesser, G. Steinmeyer:
Non-Instantaneous Polarization Dynamics in Resonant Dielectrics,
CLEO/Europe-EQEC 2015 Münich, Germany (regular talk, EE-5b.2 MON)
- H.G. Kurz, M. Kretschmar, T. Binhammer, T. Nagy, D. Ristau, M. Lein, U. Morgner, M. Kovacev:
How far does an electron travel during High-Order Harmonic Generation?,
CLEO/Europe-EQEC 2015 Münich, Germany (regular talk, CG-4.3 WED)
- A. Blumenstein, M. Kovacev, U. Morgner, P. Simon, T. Nagy:
High-sensitivity measurement of the nonlinear refractive index of noble gases,
DPG Frühjahrstagung 2015, Heidelberg, 23-27 March 2015 (regular talk)
- P. Simon:
Creation of periodic nano-structures by short laser pulses, ELI-ALPS 3rd User Workshop,
Szeged, Hungary, November 2015 (invited talk)
- F. Kleinwort, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon, C. Dölle, I. Grunwald, L. Wittig:
Nanostrukturierung von Implantat-Oberflächen zur Reduzierung der Zelladhäsion,
11.ThGOT u. 10. Thüringer Biomaterial-Kolloquium, Zeulenroda September 2015 (regular talk)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Implantation of gold into pure and silver containing glass by means of ArF-excimer laser irradiation,
Glass & Optical Materials Division and Deutsche Glastechnische Gesellschaft Joint Annual Meeting, Miami (05.2015)
- H. Stolzenburg, P. Peretzki, N. Wang, M. Seibt, J. Ihlemann:
Implantation of plasmonic nanoparticles in SiO2 by pulsed laser irradiation of gold films on SiOx-coated fused silica and subsequent thermal annealing,
E-MRS Spring meeting, Lille (05.2015)
- T. Rainer, J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laserbearbeitung von Glas: Mikrooptische Strukturen und Diffraktive Markierung
Schott Technologietag, Dünnglas als Substrat zur Strukturierung und Beschichtung, Grünenplan (05.2015)
- D. Tasche, C. Gerhard, J. Ihlemann, W. Viöl:
The influence of plasma pre-treatment on the laser ablation of fused silica,
20th International Colloquium on Plasma Processes, St. Etienne (06.2015)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Hybrid micro-optical elements by laser based fabrication of Fresnel lenses on the end face of gr adient index lenses,
4th EOS Conference on Manufacturing and Testing of Optical Components (EOSMTOC 2015), München (06.2015)
- M. Kretschmar, C. Brée, T. Nagy, H.G. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovacev:
Direct High-Order Harmonic Radiation as a Tool for the Characterization of Femtosecond Filaments,
CLEO/Europe-EQEC 2015 Münich, Germany (CG-P.9 THU), (06.2015)
- C. Dölle, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J.L. Faccioni, N. Suter, L. Wittig, F. Kleinwort, I. Grunwald:
Licht als Werkzeug: Lichtbasierte biokompatible Oberflächenfunktionalisierung zur Adhäsionsreduzierung von Zellen auf Traumaimplantaten,
Deutscher Kongress für Orthopädie und Unfallchirugie (DKOU2015), Berlin (10.2015)
- C. Dölle, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. l. Faccioni, N. Suter, L. Wittig, F. Kleinwort, I. Grunwald:
Licht als Werkzeug – Oberflächenfunktionalisierung zur Adhäsionsreduzierung von humanen Zellen auf Traumaimplantaten,
F.O.M.-Konferenz, Berlin (11.2015 )
- N. Wang, T. Fricke-Begemann, P. Peretzki, J. Ihlemann, M. Seibt:
The formation of Si nanocrystals induced by CW laser annealing of silicon-rich silicon oxide,
Microscopy Conference MC, 2015 Göttingen (09.2015)
Publications
- J. Bekesi, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
Deterministic sub-micron 2D grating structures on steel by UV-fs-laser interference patterning,
Appl. Phys. A 114, 69 (2014)
- J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
Patterned deposition of thin SiOx-films by laser induced forward transfer,
Thin Solid Films 550, 521 (2014)
- D. Wang, J. Ihlemann, P. Schaaf:
Complex patterned gold structures fabricated via laser annealing and dealloying,
Applied Surface Science 302, 74 (2014)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Silicon suboxide (SiOx): laser processing and applications,
Appl. Phys. A 117, 13 (2014)
- J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
Pulsed laser-induced formation of silica nanogrids,
Nanoscale Research Letters 9, 102 (2014)
- D. Tasche, C. Gerhard, J. Ihlemann, S. Wienecke, W. Viöl:
The impact of O/Si ratio and hydrogen content on ArF excimer laser ablation of fused silica,
J. Europ. Opt. Soc. Rap. Public. 9, 14026 (2014)
- A. Dittrich, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Laser fabrication of silica gratings by ablation and modification of silicone films,
Physics Procedia 56, 927 (2014) - L. Brusberg, M. Neitz, H. Schröder, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Fresnel micro lens array in borosilicate glass by F2 laser ablation for glass interposer application,
Proc. SPIE 8951, 89510H (2014)
- M. Dubiel, M. Heinz, M. Stiebing, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, T. Rainer:
Generation and characterization of plasmonic nanostructures in glass surfaces by means of excimer and solid state laser irradiation,
Proc. SPIE 9163, 9163-58 (2014)
- D. Köhne, T. Fricke-Begemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Large area silica nano grids by homogeneous high resolution laser patterning of SiOx-films,
Proceedings of LPM2014 – the 15th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (2014)
- F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo,
U. Morgner, P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
Compression of CEP-stable multi-mJ laser pulses down to 4 fs in long hollow fibers,
Laser Phys. Lett. 11 095401 (2014)
- M. Hoffmann, T. Nagy, T. Willemsen, M. Jupé, D. Ristau, U. Morgner:
Pulse characterization by THG d-scan in absorbing nonlinear media,
Optics Express 22, 5234-5240 (2014)
- M. Kretschmar, C. Brée, T. Nagy, A. Demircan, H.G. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovačev:
Direct observation of pulse dynamics and self-compression along a femtosecond filament,
Opt. Express 22, 22905-22916 (2014)
- F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo, U. Morgner,
P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
“3mJ, 4fs, CEP-stable pulses from long hollow fibers” International Committee on Ultra-Intense Lasers 2014, Goa, India, October 12-17 2014
- F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo, U. Morgner,
P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
“Generation of 3mJ, sub-4s CEP-stable pulses at 1kHz by long stretched hollow fiber compression” 23rd Congress of the International Commission for Optics, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 26-29 August 2104
- F. Silva, M. Miranda, B. Alonso, J. Rauschenberger, V. Pervak, H. Crespo, F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar,
A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, R. Romero, U. Morgner, P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
“The dispersion-scan technique: generation and measurement of carrier-envelope phase stabilized 3 fs single-cycle pulses and 4 fs high-energy pulses” Photon 14, Imperial College London, London, UK, 1-4 September 2014
Conference constributions
- D.S. Ivanov, V.P. Lipp, A. Blumenstein, V.P. Veiko, E. Jakovlev, M. E. Garcia, B. Rethfeld,
J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Molecular Dynamics Modeling of fs Laser Pulse Nanostructuring of Materials, ICPEPA-9,
9th International Conference on Photo-Excited Processes and Applications, Matsue, Japan (2014)
- M. Kretschmar, C. Brée, A. Demircan, T. Nagy, H.G. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovacev:
Direct observation of pulse splitting dynamics and self-compression along a femtosecond filament,
HILAS 2014, Berlin, Germany (regular talk, HTu1C.2)
- C. Brée, M. Kretschmar, T. Nagy, M. Hofmann, A. Demircan, U. Morgner, M. Kovacev:
Fingerprint of Self-Compression in the High Harmonic Spectrum from a Filament,
HILAS 2014, Berlin, Germany (poster, JW2A.7)
- F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, M. Kovacs, M. Miranda, R. Romero, H. Crespo, P. Simon,
R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
Generation of 3-mJ, 4-fs CEP-Stable Pulses by Long Stretched Flexible Hollow Fibers,
HILAS 2014, Berlin, Germany (post-deadline talk, HW5C.2)
- F. Böhle, M. Kretschmar, A. Jullien, P. Simon, R. Lopez-Martens, T. Nagy:
CEP-stable, multi-mJ, 4.3 fs pulses from long stretched flexible hollow fibers,
CLEO 2014, San José, CA, USA (regular talk, SW1E.1)
- M. Kretschmar, T. Nagy, A. Demircan, C. Brée, M. Hofmann, H.G. Kurz, U. Morgner, M. Kovacev:
Direct observation of pulse dynamics, influencing high-order harmonic emission along a filament,
CLEO 2014, San José, CA, USA (regular talk, STh1E.1)
- L. Brusberg, M. Neitz, H. Schröder, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of Fresnel micro lens array in borosilicate glass by F2-laser ablation for glass interposer application, OPTO, part of Photonics West, San Francisco (02.2014)
- D. Köhne, T. Fricke-Begemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Large area silica nano grids by homogeneous high resolution laser patterning of SiOx-films,
LPM2014 – the 15th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication Vilnius, Litauen (06.2014)
- M. Dubiel, M. Heinz, M. Stiebing, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, T. Rainer:
Generation and characterization of plasmonic nanostructures in glass surfaces by means of excimer and solid state laser irradiation,
SPIE Optics + Photonics 2014, San Diego (08.2014)
- A. Dittrich, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Laser fabrication of silica gratings by ablation and modification of silicone films 8th International Conference on Photonic Technologies, LANE 2014, Fürth (09.2014)
- J. Ihlemann:
Excimerlaser-Strukturierung von SiOx-Schichten: Herstellung von Phasenmasken und Nanonetzen,
PhotonicNet Arbeitskreistreffen DUV/VUV-Optik Braunschweig (09.2014)
- J. Meinertz, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann, M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, S. Brunsch, T. Rainer:
UV-Laser-Feinststrukturierung von Glasoberflächen und ihre Anwendung zur diffraktiven Markierung, Workshop Bearbeitung von Glaswerkstoffen mit innovativen Verfahren,
Düsseldorf (10.2014)
- T. Fricke-Begemann:
Mikrooptiken aus Glas und Quarzglas durch direkte UV-Laserbearbeitung, Handlungsfeldkonferenz Optische Kommunikation und Sensorik, Berlin (11.2014)
- M. Heinz, M. Dubiel, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, A. Hoell:
Investigation of metal nanoparticles formed by means of excimer laser irradiation of ionexchanged glasses, 88th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Glass Technology,
Aachen (05.2014)
- J. Ihlemann:
Laserstrukturierung von Phasenmasken in Quarzglas,
PhotonicNet Seminar Diffraktive optische Elemente – Einsatzfelder, Design,
Produktion und Messtechnik Göttingen (11.2014)
Book constributions
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Coupling to planar and strip waveguides. in: Planar Waveguides and other Confined Geometries, G. Marowsky,
Ed., Springer Series in Optical Sciences 189 (2014) pp. 169-183
Publications
- J. Bekesi, J. Meinertz, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
Sub-500-nm patterning of glass by nanosecond KrF-excimer laser ablation,
Appl. Phys. A 110, 17 (2013)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Laser writing of periodic nano-structures on solid surfaces,
Proc. SPIE 8796, 87962H (2013)
- J. Meinertz, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Micron and sub-micron gratings on glass by UV laser ablation,
Physics Procedia 41, 701 (2013)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
Sub-wavelength pattern generation by laser direct writing via repeated irradiation,
Optics Express 21, 626–630 (2013)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
Sub-100nm pattern generation by laser direct writing using a confinement layer,
Optics Express 21, 9017–9023 (2013)
- P. Joly, M. Petrarca, A. Vogel, T. Pohl, T. Nagy, Q. Jusforgues, P. Simon, J. Kasparian,
K. Weber, J.-P. Wolf:
Laser-induced condensation by ultrashort laser pulses at 248 nm,
Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 091112 (2013)
- A. Urban, J. Malindretos, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon, A. Rizzi:
Ga-polar GaN nanocolumn arrays with semipolar faceted tips,
New J. Phys. 15, 053045 (2013)
Conference constributions
- T. Rohrlapper, U. Morgner, P. Simon, T. Nagy:
High-energy driver pulses for high-harmonic generation,
523rd WE Heraeus Seminar: High-Harmonic Spectroscopy, Bad Honnef (02.2013)
- T. Rohrlapper, P. Simon, U. Morgner, T. Nagy:
Efficient spectral broadening of multi-mJ pulses in long hollow fibers,
CLEO®/Europe 2013, Munich, Germany, paper CD-3.1-SUN (05.2013)
- P. Simon:
Direkte Laserlithographie Workshop: Mustererzeugung und Laserstrahlformung: Technologien – Entwicklungen – Anwendungen,
vom Bayerischen Laserzentrum und bayern photonics, Nürnberg (11.2013)
- J. Meinertz, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Micron and sub-micron gratings on glass by UV laser ablation
Lasers in Manufacturing,
Conference 2013 München (05.2013)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, M. Wiesner, J. Ihlemann:
Laser based fabrication of high precision fused silica phase masks,
3rd EOS Conference on Manufacturing of Optical Components
München (05.2013)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann:
Silicon Suboxide (SiOx) – Laser Processing and Applications,
12th International Conference on Laser Ablation (COLA)
Ischia (10.2013)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Direct Laser Lithography – Laser writing of periodic nano-structures,
Workshop Mustererzeugung und Laserstrahlformung
Nürnberg (11.2013)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser-Mikrostrukturierung von Glasoberflächen und dielektrischen Schichten,
Workshop Laserbearbeitung von Glaswerkstoffen
Hannover (11.2013)
- D. Wang, J. Ihlemann, P. Schaaf:
Complex patterned gold structures fabricated via laser annealing and dealloying,
EMRS Spring Meeting
Strasbourg (06.2013)
Publications
- J. Hoffmeister, C. Gerhard, S. Brückner, J. Ihlemann, S. Wieneke, W. Viöl:
Hybrid Laser-Plasma Micro-Structuring of Fused Silica Based on Surface Reduction by a Low-Temperature Atmospheric Pressure Plasma,
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 7, 73 (2012)
- A. Syring, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
F2-laser modification and patterning of silicone films,
Applied Surface Science 261, 68 (2012)
- J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz, G. Danev:
Excimer laser ablation of thick SiOx-films: etch rate measurements and simulation of the ablation threshold,
Applied Physics Letters 101, 091901 (2012)
- J. Hoffmeister, C. Gerhard, S. Brückner, J. Ihlemann, S. Wieneke, W. Viöl:
Laser Micro-Structuring of Fused Silica Subsequent to Plasma-Induced Silicon Suboxide Generation and Hydrogen Implantation,
Physics Procedia 39, 613 (2012)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
Sub-wavelength pattern generation by laser direct writing via repeated irradiation,
Opt. Express, accepted for publication (2012)
Conference constributions
- M. Petrarca, S. Henin, T. Nagy, A. Vogel, J. Kasparian, P. Simon, J.-P. Wolf:
High-efficiency particle nucleation by ultrashort UV pulses,
COFIL 2012 4th International Symposium on Filamentation Tucson, Arisona October 2012
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
Laser writing of periodic nano-structures on solid surfaces,
The 2nd International Symposium on Laser Interaction with Matter, (LIMIS 2012), Xi’an, China, September 2012
- T. Nagy, M. Kovacev, U. Morgner, P. Simon:
Pulse compression in long hollow fibers,
DPG Frühjahrstagung, March 2012, Stuttgart
- J. Ihlemann:
Herstellung diffraktiver optischer Elemente mittels Excimerlaserablation,
Workshop Formung von Laserstrahlung
Nürnberg (04.2012)
- A. Syring, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of silica micro patterns by F2-laser modification and ablation of silicone films,
13th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM 2012) Washington DC, USA (06.2012)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laserstrukturierung von Oberflächen und Schichten für optische Anwendungen,
PhotonicNet Arbeitskreis Oberflächenbearbeitung,
Göttingen (06.2012)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser-Mikro- und Nanostrukturierung transparenter Materialien und dielektrischer Beschichtungen,
Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung
Berlin (10.2012)
- J. Ihlemann:
UV-Laser-Mikrostrukturierung von Glas und dielektrischen Beschichtungen,
Schott Technologietag
Grünenplan (11.2012)
- J. Hoffmeister, C. Gerhard, S. Brückner, J. Ihlemann, S. Wieneke, W. Viöl:
Laser Micro-Structuring of Fused Silica Subsequent to Plasma-Induced Silicon Suboxide Generation and Hydrogen Implantation,
7th International Conference on Photonic Technologies (LANE 2012)
Fürth (11.2012)
Book constributions
- G. Marowsky, P. Simon, K. Mann, C. K. Rhodes:
Ultraviolet Lasers: Excimers, Fluorine (F2), and Nitrogen (N2),
in: Springer Handbook of Lasers and Optics, ed. by F. Träger 2nd edn. (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 2012) pp. 832-852, Chap. 11.7
Publications
- M. Wiesner, J. Ihlemann:
High resolution patterning of sapphire by F2-laser ablation,
Appl. Phys. A 103 (2011), 51
- J. Richter, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
Patterned laser annealing of silicon oxide films,
Appl. Phys. A 104 (2011), 759
- T. Nagy, V. Pervak, P. Simon:
Optimal pulse compression in long hollow fibers,
Opt. Lett. 36 (2011), 4422
Conference constributions
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
Long hollow fibers for strong, spatially uniform spectral broadening of ultrashort pulses,
CLEO/Europe, Munich (May.2011)
- J. Ihlemann, J. Bekesi, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
Periodische Oberflächenstrukturen auf Metallen und Halbleitern durch UV-Femtosekunden- und Pikosekunden-Laserbearbeitung,
PhotonicNet Arbeitskreis Oberflächenbearbeitung, Göttingen (03.2011)
- J. Ihlemann:
Excimer laser ablation patterning: micro- and nanostructures for optical applications,
Inauguration Laser Center EMPA, Thun (04.2011)
- J. Ihlemann:
F2-Laser-Mikrostrukturierung von Glas für optische Anwendungen,
Workshop Laserbearbeitung von Glaswerkstoffen, Erlangen (04.2011)
- M. Wiesner, J. Ihlemann:
Fabrication of sapphire micro optics by F2-laser ablation,
Lasers in Manufacturing, München (05.2011) - J. Ihlemann:
Excimer laser ablation patterning: micro- and nanostructures for optical and biosensor applications,
Institut für Nanostrukturtechnologie und Analytik, Kassel (06.2011)
Publications
- B. Borchers, J. Bekesi, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
“Submicron surface patterning by laser ablation with short UV pulses using a proximity phase mask setup”, J. Appl. Phys. 107 (2010), 063106
- J. Bekesi, J.J.J. Kaakkunen, W. Michaeli, F. Kleiber, M. Schoengart, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Fast fabrication of super-hydrophobic surfaces on polypropylene by replication of short-pulse laser structured molds”, Appl. Phys. A 99 (2010), 691
- J.J.J. Kaakkunen, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Ablation of microstructures applying diffractive elements and UV femtosecond laser pulses”, Appl. Phys. A 101 (2010), 225
- J. Bekesi, J.J.J. Kaakkunen, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Fabrication of DOEs and their application for parallel laser processing of functional surfaces”, Laser Optics Berlin, Berlin (March 2012)
- T. Nagy, W. Schweinberger, A. Sommer, M. Schultze, R. Kienberger, F. Krausz, P. Simon:
“Novel hollow fiber compressor for high power, multi-mJ ultrafast lasers”, XXXI ECLIM, 31st European Conference on Laser Interaction with Matter, Budapest (September 2010)
- K. Christou, I. Knorr, J. Ihlemann, H. Wackerbarth, V. Beushausen:
“Fabrication and Characterization of Homogeneous SERS-Substrates by Single Pulse UV-Laser Treatment of Gold and Silver Films”, Langmuir 26, 18564 (2010)
- J. Bekesi, J. Kaakkunen, W. Michaeli, F. Klaiber, M. Schoengart, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Fast Fabrication of Super-hydrophobic Surfaces on Polypropylene by replication of short pulse laser structured molds”, Applied Physics A 99, 691 (2010)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
“Microstructured GRIN lens as an external coupler to thin-film waveguides”, Proceedings LPM 2010, paper #10-80
- M. Wiesner, H.H. Müller, E. Lankenau, G. Hüttmann, J. Ihlemann:
“Laser micromachining process control by optical coherence tomography”, Proceedings LPM2010, paper #10-41
- J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
“Laser induced congruent forward transfer of SiOx-layers”, Applied Physics A 101, 483 (2010)
- M. Jahn, J. Richter, R.Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
“Ablation of silicon suboxide thin layers”, Applied Physics A 101, 533 (2010)
- J. Kaakkunen, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Ablation of microstructures applying diffractive elements and UV femtosecond laser pulses”, Applied Physics A 101, 225 (2010) J. Ihlemann: “Laser Micromachining”, In: Laser Materials Processing – Fundamentals, Applications and Developments, P. Schaaf Editor, Springer Series in Materials Science 139, 169-187, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2010)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann:
“Direct light-coupling to thin-film waveguides using a grating-structured GRIN lens”, Optics Express 18, 19860 (2010)
- J. Ihlemann:
“Micromachining and patterning”, In: Laser Precision Microfabrication, K. Sugioka, M. Meunier, A. Piqué Editors Springer Series in Materials Science 135, 239-257, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2010)
- R. Bäumner, L. Bonacina, J. Enderlein, J. Extermann, T. Fricke-Begemann, G. Marowsky, J.-P. Wolf: “Evanescent-field-induced second harmonic generation by noncentrosymmetric nanoparticles”, Optics Express 22, 23218 (2010)
- J. Zinn, M. Schütte, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
“F2-laser fabrication of fiber-integrated optical elements”, Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 5, 6 (2010)
- B. Borchers, J. Bekesi, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
“Sub micron surface patterning by laser ablation with short UV pulses using a proximity phase mask setup”, Journal of Applied Physics 107, 063106 (2010)
- M. Wiesner, J. Ihlemann, H.H. Müller, E. Lankenau, G. Hüttmann:
“Optical coherence tomography for process control of laser micro machining”, Review of Scientific Instruments 81, 033705 (2010)
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
“Single-shot TG FROG for the characterization of ultrashort DUV pulses”, Opt. Express 17, 8144 (2009)
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
“Generation of High-Energy Sub-20-fs DUV Pulses in Noble-Gas-Filled Hollow Fiber”, in The Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO)/The International Quantum Electronics Conference (IQEC) (Optical Society of America, Washington, DC, 2009), CFN7
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
“Generation and characterization of energetic sub-20-fs DUV Pulses”, in 2009 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & the European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe – EQEC 2009), CF7.3 THU
- T. Nagy, P. Simon:
“Generation of 200-µJ, sub-25-fs deep-UV pulses using a noble-gas-filled hollow fiber”, Opt. Lett. 34, 2300 (2009)
- P. Zahariev, N. Mechkarov, G. Danev, J. Ihlemann:
“Excimer laser induced micro bumps on preheated BK7-glass”, Applied Physics A 95, 639 (2009)
- J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
“Laser Based Rapid Fabrication of SiO2-phase Masks for Efficient UV-laser Micromachining”, Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 4, 100 (2009)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, R. Bäumner, K. Bodensiek, A. Selle:
“Coupling efficiency of fluorescent molecules to a sensing waveguide”, DGaO Proceedings 2009 – www.dgao-proceedings.de – ISSN: 1614-8436 (2009)
- R. Bäumner, K. Bodensiek, A. Selle, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky:
“Efficiency of fluorescence coupling into planar waveguides”, Proc. SPIE 7368-26 (2009)
- J. Zinn, M. Schütte, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
“F2-laser fabrication of fiber-integrated optical elements”, Proceedings of LAMP2009 – the 5th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (2009)
- J. Bekesi, J. Kaakkunen, J. Meinertz, T. Omairi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Rapid Fabrication of Functional Surfaces by Parallel Laser Processing Using DOEs”, Proceedings of LAMP 2009 – the 5th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing Martin Jahn, “Untersuchung der Laserablation dünner Metall- und Oxidschichten in unterschiedlichen Umgebungsmedien”, Bachelorarbeit, TU Ilmenau (2009)
- T. Nagy, M. Forster, P. Simon:
„Flexible hollow fiber for pulse compressiors”, Applied Optics 47, 3264-3268 (2008)
- J. Bekesi, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„Fabrication of large area grating structures through laser ablation”, Appl. Phys. A, 93, 27 (2008)
- P. Simon:
„Erzeugung periodischer Sub-Mikrometer-Strukturen durch Laserablation“, eingeladener Vortrag, Insitutskolloquium, Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Berlin, März 2008
- P. Simon:
„Fabrication of periodic nanostructures through direct laser ablation”, ISL 2008 International Symposium on Laser-Micromachining, November 2008, Chemnitz
- J. Ihlemann, J. Békési, J.-H.Klein-Wiele, P.Simon:
„Processing of dielectric optical coatings by nanosecond and femtosecond UV laser ablation”, Laser Chemistry (2008)
- J. Bekesi, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„Grating Interferometers for Efficient Generation of Large Area Grating Structures via Laser Ablation”, Proceedings of LPM2007-the 8th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication, p 1-4, (2007)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H Klein-Wiele, J Bekesi, P Simon:
„UV Ultrafast Laser Processing using Phase Masks”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 59 449–452, (2007)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon:
„SiO2 phase gratings fabricated by UV laser ablation patterning”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 6462B, paper # 41 (2007)
- T. Nagy, M. Forster, P. Simon:
„Generation of high-energy sub-20 fs pulses at 248 nm”, CLEO/Europe 07 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Munich, paper CF5-2-WED (2007)
- J. Bekesi, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„Fabrication of large area grating structures through laser ablation using a grating-interferometer setup”, COLA 2007, 9th International Conference on Laser Ablation, Tenerife, Spain, Technical Program, p.28
- M.A. Bader, A. Selle, O. Stenzel, R. Delmdahl, G. Spiecker, C. Fischer:
“High spectral resolution analysis of tunable narrowband resonant grating waveguide structures”, Appl. Phys. B 89, 151–154 (2007)
- J. Ihlemann, M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg, T. Fricke-Begemann:
“Micro patterning of fused silica by ArF- and F2-laser ablation”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 59, 206 (2007)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon:
“UV Ultrafast Laser Processing Using Phase Masks”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 59, 449 (2007)
- N. Mainusch, C. Pflugfelder, J. Ihlemann, W. Viöl:
“Plasma-jet Coupled with Nd:YAG Laser: New Approach to Surface Cleaning”, Plasma Processes and Polymers 4, S33 (2007)
- J. Ihlemann:
“UV-laser ablation of fused silica mediated by solid coating absorption”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 6458A, paper # 14 (2007)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon:
SiO2 phase gratings fabricated by UV laser ablation patterning Proc. SPIE Vol. 6462B, paper # 41 (2007)
- J. Li, J. Dou, P.R. Herman, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky:
“Deep ultraviolet Laser micromachining of novel fibre optic devices”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 59, 691 (2007)
- M. Rauh, J. Ihlemann, A. Koch:
“Laser Surface Roughening of PTFE for Increased Bonding Strength”, Applied Physics A 88, 231 (2007)
- J. Békési, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Grating Interferometers for Efficient Generation of Large Area Grating Structures via Laser Ablation”, Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 2, 221 (2007)
- M. A. Bader, A. Selle, O. Stenzel, R. Delmdahl. G. Spiecker, C. Fischer:
“High spectral resolution analysis of tunable narrowband resonant grating waveguide structures”, Applied Physics B 89, 151 (2007)
- R .F. Delmdahl, G. Spiecker, M.A. Bader, A. Selle:
“Spectral resolution analysis of resonant grating waveguides”, Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 38 (3), 218 (2007)
- M. Schütte:
“Herstellung und Charakterisierung optisch funktionaler Oberflächen auf Faserendflächen”, Masterarbeit, Göttingen (2007)
- M.A. Bader, C. Kappel, A. Selle, J. Ihlemann, M.L. Ng, P.R. Herman:
“F2-laser machined submicrometer gratings in thin dielectric films for resonant waveguide applications”, Applied Optics 45, 6586 (2006)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
“Fabrication of SiO2 phase gratings by UV laser patterning of siliconsuboxide layers and subsequent oxidation”, Online Proceedings of LAMP (2006)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, J. Meinertz:
“Diffraktive Mikrolinsen: Herstellung durch direkte Laserablation”, DGaO-Proceedings P16 (2006)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Bertram, M. Hottenrott, J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever:
“Modularer Fluoreszenz-Reader zur parallelen Analyse von Protein-Chips In: Technische Systeme für Biotechnologie und Umwelt”, D. Beckmann, M. Meister Hrsg., Tagungsband des 13. Heiligenstädter Kolloquium, 2006, S. 149-153
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
“Fabrication of SiO2 phase gratings by UV laser patterning of silicon suboxide layers and subsequent oxidation”, Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 1, 221 (2006)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann:
“Fabrication of diffractive micro lenses by direct laser ablation Proceedings of the EOS Topical Meeting on Micro-Optics”, Diffractive Optics and Optical MEMS (17 – 19 October 2006, Paris, France), p. 114 (2006)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon:
“Laser fabricated SiO2 phase gratings for high resolution surface patterning”, Proceedings of the EOS Topical Meeting on Micro-Optics, Diffractive Optics and Optical MEMS (17 – 19 October 2006, Paris, France), p. 150 (2006)
- M. Wiesner:
“Entwicklung eines Messsystems zur Charakterisierung von partiell kohärenten Strahlungsquellen”, Masterarbeit, Göttingen 2006
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, T. Nagy, P. Simon:
„Hollow-Fiber Pulse Compressor for KrF Lasers”, Appl. Phys B 82, 567-570 (2006)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, Peter Simon J. Ihlemann:
„Fabrication of SiO2 phase gratings by UV laser patterning of silicon suboxide layers and subsequent oxidation, The 4th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing”, LAMP 2006, May 16-19, 2006, Kyoto Research Park, Kyoto, Japan
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele:
„Fabrication of sub-wavelength-period nanostructures with UV femtosecond laser ablation, The 4th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing”, LAMP 2006, May 16-19, 2006, Kyoto Research Park, Kyoto, Japan
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon, J. Ihlemann:
„Fabrication of SiO2 phase gratings by UV laser patterning of silicon suboxide layers and subsequent oxidation”, Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering 1, 221 (2006)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
„Enhancement of Laser Nano-Patterning of Semiconductors: Direct Ablation of PMMA Coated Silicon”, CLEO/QELS and PhAST 2006, May 21–May 26, 2006 Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach, California
- P. Simon:
„Material processing with UV femtosecond pulses, 1st International Symposium on Laser-Micromachining”, ISL Chemnitz, (2006)
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, P. Simon:
„Laser fabricated SiO2 phase gratings for high resolution surface patterning, Proceedings of the EOS Topical Meeting on Micro-Optics, Diffractive Optics and Optical MEMS”, (17-19 October 2006, Paris, France), p. 150 (2006)
- J. Ihlemann:
“UV laser ablation patterning of oxide films for optical applications”, Optical Engineering 44, 051108 (2005)
- M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg, J. Ihlemann, J. Heber:
“Laser patterning of SiOX-layers for the fabrication of diffractive phase elements for deep UV applications”, Appl. Surf. Sci. 248, 190 (2005)
- F. Balzer, J. Ihlemann, A.C. Simonsen, H.-G. Rubahn:
“UV Laser cutting of organic nanofibers”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5720, 165 (2005)
- M. Wehner, M. Hessling, J. Ihlemann:
“Ablative Micro Fabrication”, in: Excimerlaser Technology, D. Basting, G. Marowsky, Eds., Springer Verlag (2005)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“Nano-structuring by femtosecond excimer laser pulses”, in: Excimerlaser Technology, D. Basting, G. Marowsky, Eds., Springer Verlag (2005)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Li, J. Dou, J. Ihlemann, P. R. Herman, G. Marowsky:
“Laser machining of micro-lenses on the end face of optical fibers”, Proc. of the Third International WLT-Conference Lasers in Manufacturing, LIM 2005, p. 733 A. Selle,
- C. Kappel, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky, K. Winkler, U. Alexiev:
“Picosecond-pulse-induced two-photon fluorescence enhancement in biological material by application of grating waveguide structures”, Optics Letters 30, 1683-1685 (2005)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
“High speed fabrication of periodic nanostructures”, Proc. of the Third International WLT-Conference Lasers in Manufacturing, LIM 2005, p. 477
- J. Ihlemann:
“Patterning of oxide thin films by UV laser ablation”, Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials 7, 1191 (2005)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, R. Weichenhain-Schriever, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky:
“Mikrolinsen auf Glasfasern”, Laser + Photonik 2/2005, 24
- T. Fricke-Begemann, M. A. Bader, J. Ihlemann, C. Kappel, J. Meinertz, A. Selle:
“Two-photon fluorescence: large area excitation and enhanced sensitivity using waveguide structures”, Proc. DGaO 2005, B24
- J. Heber, J. Ihlemann, M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg, J. Schmidt:
“Laser ablation of SiOx thin films for direct mask writing”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5963, 594 (2005)
- M. Rauh:
“UV-Laser-Mikrostrukturierung von Polytetrafluorethylen für biophysikalische Anwendungen”, Masterarbeit, Göttingen (2005)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„Nanostructuring with Femtosecond Excimer Laser Pulses” in: “Excimer Laser Technology” D. Basting, G. Marowsky, Eds., Springer Verlag (2005)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Békési, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„High speed fabrication of periodic nanostructures”, Proc. of the Third International WLT-Conference Lasers in Manufacturing, LIM 2005, p. 477
- J. Bekesi, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:
„Femtosecond UV Laser Manufacturing of Nano Structures”, German-Canadian Workshop “Laser in Manufacturing”, Munich, June 2005
- J. Ihlemann, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon:
„UV Ultrafast Laser Processing Using Phase Masks”, COLA 2005, 11.-16.9.2005, Banff, Canada
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, T. Nagy, P. Simon:
„Hollow-Fiber Pulse Compressor for KrF Lasers”, Appl. Phys B, DOI: 10.1007/s00340-005-2074-0 (2005)
- T. Nagy, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon:
„Towards the Generation of Energetic Sub-20 fs DUV Pulses”, Physics Colloquium, China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing, China, December 2005
- T. V. Murzina, F.Yu. Sychev, E.M. Kim, E.I. Rau, S.S. Obydena, O.A. Aktsipetrov, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky:
„One-dimensional photonic crystals based on porous n-type silicon”, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 123702 (2005)
- E.M. Kim, S.S. Elovikov, T.V. Murzina, A.A. Nikulin, O.A. Aktsipetrov, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Surface-enhanced optical third-harmonic generation in Ag island films”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 227402 (2005)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky:
„Double grating waveguide structures: 350-fold enhancement of two-photon fluorescence applying ultrashort pulses”, Sensors and Actuators B 107, 135-139 (2005)
- S. Soria, A. Thayil, G. Badenes, M.A. Bader, A. Selle, G. Marowsky:
„Resonant double grating waveguide structures as enhancement platforms for two-photon fluorescence excitation”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 081109 (2005)
- A. Thayil, S. Soria, G. Badenes, T. Katchalski, A.A. Friesem, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Two-photon fluorescence spectroscopy by resonant single and double grating waveguide structures”, in Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/Quantum Electronics and Laser Science and Photonic Applications, Systems and Technologies 2005 (Optical Society of America, Washington, 2005), CTuH2
- A. Selle, C. Kappel, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky, K. Winkler, U. Alexiev:
„Picosecond-pulse-induced two-photon fluorescence enhancement in biological material by application of grating waveguide structures”, Opt. Lett. 30, 1683-1685 (2005)
- K. Winkler, A. Selle, C. Kappel, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky, U. Alexiev:
„Picosecond pulse induced two-photon fluorescence enhancement in biological material applying grating waveguide structures”, Biophysical Society, 49th Annual Meeting, Long Beach, Californien, USA, Februar 12-16, 2005 (Vortrag)
- K. Winkler, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky, U. Alexiev:
„Picosecond pulse induced two-photon fluorescence enhancement in biological material applying grating waveguide structures: Towards the elucidation of MHC-Antigen recognition in living cells”, Joint meeting of Swiss and German Biophysicists: “Molecular basis of signal information and energy transduction in biomolecules”, Bonifatiuskloster, Hünfeld, Deutschland, Mai 5-7, 2005 (Vortrag)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, M.A. Bader, J. Ihlemann, C. Kappel, J. Meinertz, A. Selle:
„Two-photon fluorescence: large area excitation and enhanced sensitivity using waveguide structures”, 106. Tagung der DGaO, Wroclaw, Polen, Mai 17-21, 2005 (Vortrag)
- A. Thayil, S. Soria, G. Badenes, T. Katchalski, A.A. Friesem, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Two-Photon Fluorescence Spectroscopy by Resonant Single and Double Grating Waveguide Structures”, CLEO/QELS and PhAST 2005, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, Mai 22-27, 2005 (Vortrag)
- J. Ihlemann, D. Schäfer: “Patterning of optical coatings by laser ablation for the fabrication of dielectric masks and diffractive phase elements”, Journal of Microlithography, Microfabrication and Microsystems 3, 455 (2004)
- F. Beinhorn, J. Ihlemann, K. Luther, J. Troe: “Plasma effects in picosecond-femtosecond UV laser ablation of polymers”, Applied Physics A 79, 869 (2004)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon:”Nano-Fabrication of Solid Materials with Ultraviolet Femtosecond Pulses”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5399, 139 (2004)
- Y. Kaganovskii, I. Antonov, M. Rosenbluh, J. Ihlemann, A. A. Lipovskii: “Two- and three-dimensional photonic crystals produced by pulsed laser irradiation in silver-doped glass”, Solid State Phenomena 99-100, 65 (2004)
- K. Rubahn, J. Ihlemann, G. Jakopic, A.C. Simonsen, H.-G. Rubahn: “UV laser induced grating formation in PDMS thin films”, Applied Physics A 79, 1715 (2004)
- J. Ihlemann, F. Beinhorn, H. Schmidt, K. Luther, J. Troe: “Plasma and plume effects on UV laser ablation of polymers”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5448, 572 (2004)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, R. Weichenhain: “Mikrooptiken zur Verbesserung eines optischen Abstandsensors und Mikrofon”, Proc. DGaO (2004)
- J. Ihlemann, M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg, T. Fricke-Begemann: “UV-Laserablation von Quarzglas zur Herstellung diffraktiver optischer Elemente”, Proc. DGaO (2004)
- T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky, J. Li, P. R. Herman: “Micro-lens machining on optical fibers by direct laser ablation”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5578, 589 (2004)
- M. A. Bader, C. Kappel, A. Selle, J. Ihlemann, M.L. Ng, P.R. Herman: “Fabrication of sub-micron gratings in ultrathin films by 157-nm laser ablation and their application as grating waveguide structures”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5578, 559 (2004)
- G. Marowsky, M. A. Bader, A. Selle, C. Kappel, T. Fricke-Begemann, J. Meinertz, J. Ihlemann: “Neue Perspektiven der Zwei-Photonen-Technologie”, In: Technische Systeme für Biotechnologie und Umwelt, D. Beckmann, M. Meister Hrsg., Tagungsband des 12. Heiligenstädter Kolloquium, S. 119 (2004)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, T. Fricke-Begemann, M. A. Bader, G. Marowsky: “Giant enhancement of two-photon fluorescence induced by resonant double grating waveguide structures”, Applied Physics B 79, 531 (2004)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon: „Sub-Micron Machining of Solid Materials with Ultraviolet Femtosecond Pulses”, 2nd European Conference on Applications of Femtosecond Lasers in Materials Science “FemtoMat”, Bad Kleinkirchheim, Austria, February 2004
- Y. Prior, K. Zhang, V. Batenkov, Y. Paskover, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon: „Optimized pulse duration for femtosecond laser ablation”, High-Power Laser Ablation 2004, SPIE International Conference, Taos, USA, April 2004, [5448?151]
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon: „Sub-micron patterning of solid materials with ultraviolet femtosecond pulses”, Appl. Phys. A 79, 775-778 (2004)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon: „Nanofabrication of solid materials with ultraviolet femtosecond pulses”, LPM 2004 – The 5th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication Nara, Japan, May 2004
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon: „Nanofabrication of solid materials with ultraviolet femtosecond pulses”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5399, p. 139-146, (2004) Laser-Assisted Micro- and Nanotechnologies ‘03
- P. Simon: “The excimer laser as a short pulse amplifier – a powerful tool for the generation of high intensities and nano-scale structures”, Physics Colloquium, Vienna University of technology, Vienna, Austria, March 17 (2004)
- P. Simon: „The excimer laser as a short pulse amplifier – a powerful tool for the generation of high intensities and nano-scale structures”, Physics Colloquium, Max Born Institute, Berlin, Germany, May 5 (2004)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Resonant double-grating waveguide structures as inverted Fabry-Perot interferometers”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21, 1127-1136 (2004)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, T. Fricke-Begemann, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Giant enhancement of two-photon fluorescence induced by resonant double grating waveguide structures”, Appl. Phys. B 79, 531-534 (2004)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Double grating waveguide structures: 350-fold enhancement of two-photon fluorescence applying ultrashort pulses”, Sensors and Actuators B, in press (2004)
- M.A. Bader, C. Kappel, A. Selle, J. Ihlemann, M.L. Ng, P.R. Herman: „Fabrication of sub-micron gratings in ultrathin films by 157-nm laser ablation and their application as grating waveguide structures”, Proc. SPIE 5578, 559-567 (2004)
- C. Kappel, A. Selle, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Ultrashort-pulse behavior in resonant reflection filters”, Proc. SPIE 5577, 716-723 (2004)
- E.M. Kim, S.S. Elovikov, T.V. Murzina, O.A. Aktsipetrov, M.A. Bader, G. Marowsky: „Giant third optical harmonic generation in island silver films”, JETP Lett. 80, 527-531 (2004)
- Yu. G. Fokin, T.V. Murzina, O.A. Aktsipetrov, S. Soria, G. Marowsky: „Ferroelectric ordering and electroclinic effect in chiral smectic liquid crystals”, Phys. Rev. E 69, 031701 (2004)
- M.G. Martemyanov, E.M. Kim, T.V. Dolgova, A.A. Fedyanin, O.A. Aktsipetrov, G. Marowsky: „Third-harmonic generation in silicon photonic crystals and microcavities”, Phys. Rev. B 70, 073311 (2004)
- S. Soria, T. Katchalski, E. Teitelbaum, A.A. Friesem, G. Marowsky: “Enhanced two-photon fluorescence excitation by resonant grating waveguide structures”, Opt. Lett. 29, 1989-1991 (2004)
- J. Békési, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, D. Schäfer, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon: „Surface texturing of metals with sub-micron precision using a short pulse UV laser”, SPIE Vol. 4830, 497 (2003)
- J. Bekesi, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon: „Efficient submicron processing of metals with femtosecond UV pulses”, Appl Phys A 76, 3, 355-357 (2003)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon: „Nano-fabrication of solid materials with ultraviolet femtosecond pulses”, X. International Conference on Laser-Assisted Micro- and Nanotechnologies, LAM-X, St. Petersburg, July 2003, invited talk
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon: „Sub-micron sized periodic 3-D surface structures generated by single femtosecond UV laser pulses”, Laser Precision Microfabrication, LPM 2003, June 2003, Munich
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, J. Bekesi, P. Simon: „Sub-micron patterning of solid materials with ultraviolet femtosecond pulses”, 7th International Conference on Laser Ablation, Hersonissos, Crete, Greece, October 2003, invited talk
- C. Dölle, C. Reinhardt, P. Simon, B. Wellegehausen: „Spectral phase matching for highly efficient frequency tripling of short-pulse KrF laser radiation in argon”, Appl. Phys. B 76, 891-895 (2003)
- J. Békési, D. Schäfer, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon: „Fabrication of diffractive optical elements by ArF laser ablation of fused silica”, SPIE Vol. 4977, 235 (2003)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon: „Fabrication of periodic nanostructures by phase-controlled multiple-beam interference”, Applied Physics Letters 83, 4707-4709 (2003)
- J.-H. Klein-Wiele, P. Simon: „Fabrication of periodic nanostructures by phase-controlled multiple-beam interference”, Virtual Journal of Nanoscale Science & Technology Volume 8, Issue 24 “Advances in Fabrication and Processing”
- J. Ihlemann, S. Müller, S. Puschmann, D. Schäfer, M. Wei, J. Li, P.R. Herman, “Fabrication of submicron gratings in fused silica by F2-laser ablation”, Applied Physics A 76, 751 (2003)
- J. Ihlemann, S. Müller, S. Puschmann, D. Schäfer, P. R. Herman, J. Li, M. Wei: “F2-laser microfabrication of sub-µm gratings in fused silica”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 4941, 94 (2003)
- J. Békési, J.-H. Klein-Wiele, D. Schäfer, J. Ihlemann, P. Simon: “Surface texturing of metals with sub-micron precision using a short pulse UV laser”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 4830, 497 (2003)
- Y. Kaganovskii, I. Antonov, D. Ianetz, M. Rosenbluh, J. Ihlemann, S. Müller, G. Marowsky, A.A. Lipovskii: “Mass transfer in optical nanocomposites induced by pulsed laser irradiation”, Solid State Phenomena 94, 105-114 (2003)
- M. Behdani, S.H. Keshmiri, S. Soria, M.A. Bader, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky, Th. Rasing: “Alignment of liquid crystals with periodic submicron structures ablated in polymeric and indium tin oxide surfaces”, Applied Physics Letters 82, 2553 (2003)
- G. Danev, E. Spassova, J. Assa, I. Karamancheva, A. Paskaleva, K. Popova, J. Ihlemann: “Properties of vacuum-deposited polyimide films”, Vacuum 70, 37 (2003)
- Yu. Kaganovskii, I. Antonov, D. Ianetz, M. Rosenbluh, J. Ihlemann, S. Müller, G. Marowsky, A.A. Lipovskii: “Optical recording in silver-doped glasses by a femtosecond laser”, Applied Physics Letters 83, 554 (2003)
- J. Békési, Dirk Schäfer, Jürgen Ihlemann, Peter Simon: “Fabrication of diffractive optical elements by ArF-laser ablation of fused silica”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 4977A, 235 (2003)
- J. Ihlemann, Dirk Schäfer: “Laser ablation patterning of layered systems – a method to fabricate dielectric masks and diffractive phase elements”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 4984, 219 (2003)
- P. R. Herman, J. Li, A. H. Nejadmalayeri, M. Li Ng, A. Yick, J. Ihlemann: “Nano-milling of diffractive optics by F2-laser ablation”, CLEO/Europe 2003, Technical Digest (2003)
- M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg, J. Ihlemann, G. Marowsky, A. H. Nejadmalayeri, M. L. Ng, J. Li, P. R. Herman: “Fabrication of diffractive phase elements by F2-laser ablation of fused silica”, Proc. SPIE Vol. 5063, 113 (2003)
- P. R. Herman, Jianzhao Li, Kevin P. Chen, Midori Wei, Jie Zhang, J. Ihlemann, D. Schäfer, G. Marowsky, P. Oesternlin, B. Burghardt: “F2-Lasers: High resolution micromachining system for shaping photonic components”, Zugo Photonics “Insights”, Vol. 2, Issue (2003)
- M. Schulz-Ruhtenberg: “Untersuchung der Photoablation von Quarzglas mit ArF- und F2-Excimerlasern”, Diplomarbeit, Universität Göttingen, (2003)
Cooperations
Industrial cooperation partners
- Plan Optik AG
- Qioptiq Photonics GmbH & Co. KG
- Active Fiber Systems GmbH
- Dioptic GmbH
- HEGLA boraident GmbH & Co KG
- Henke-Sass Wolf GmbH
- IBL Gesellschaft für Ingenieurdienstleistungen mbH
- Innovavent GmbH
- deineMaschine
- Rio GmbH
- Thieme GmbH & Co. KG
- TRUMPF Scientific Lasers GmbH + Co. KG
- U-NICA Solutions AG, Schweiz
- Ultrafast Innovations GmbH
Cooperation partners
- Hochschule Aschaffenburg
- Fraunhofer-Institut für Photonische Mikrosysteme (IPMS)
- ICFO – The Institute of Photonics Sciences, Barcelona, Spain
- Hochschule Offenburg
- Klinikum Universität Göttingen, UMG
- Laboratoire d’Opticque Appliquée (LOA)
- Mads Clausen Institut, NanoSYD, Syddansk Universitet
- Universität Szeged, Institut für Experimentalphysik
- Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT)
- TU Kaiserslautern
- Universität Göttingen (Georg-August Univ.)
- Universität Kassel
- Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaft und Kunst (HAWK)
- Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optic und Kurzzeitspektroskopie
- Max-Planck-Institut für biophysikalische Chemie